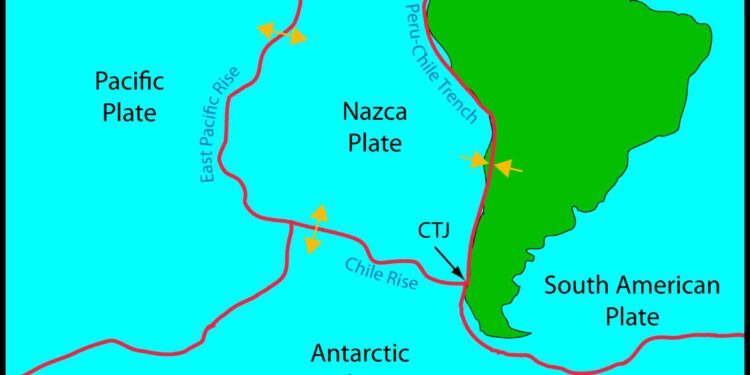
In a groundbreaking study that promises to reshape our understanding of tectonic processes, researchers are turning their attention to the Chile Triple Junction, a region where the Nazca, South American, and Antarctic tectonic plates converge. New insights from seismology are shedding light on the enigmatic “slab window” phenomenon, a geological occurrence that could explain the peculiar seismic behavior in this area. As scientists delve deeper into the complexities of plate interactions, their findings could have significant implications for predicting seismic activity not only in Chile but in subduction zones around the globe. In this article, we explore how cutting-edge seismological techniques are unraveling the mysteries of the Chile Triple Junction and what this means for our understanding of Earth’s dynamic crust.
Understanding the Significance of the Chile Triple Junction in Seismology
Located at the convergence of three tectonic plates-the Nazca, South American, and Antarctic plates-Chile’s Triple Junction is an intriguing geophysical feature that plays a pivotal role in understanding seismic behavior. This area is characterized by complex interactions between these plates, creating a dynamic environment where seismic events are not just common but also display unique patterns that differ from other regions of the world. Recent research highlights the significance of “slab windows,” which are areas where the descending oceanic crust is altered or disappears due to the divergent movement of tectonic plates. This phenomenon drastically influences stress accumulation and release patterns, leading to a better understanding of earthquake prediction and risk assessment in the region.
Scientists have noted that the seismic activity near the Chile Triple Junction can be linked to variations in the geological structure presented by these slab windows. By analyzing extensive data from seismographs and geological surveys, researchers can identify commonalities in seismic waves emanating from this area. The Triple Junction region has shown distinct characteristics that include:
- Frequency of Seismic Activity: Higher than the global average.
- Magnitude of Earthquakes: Often exceeding 7.0 on the Richter scale.
- Post-Seismic Events: Trends suggest patterns that can aid in predicting aftershocks.
Understanding these factors not only aids in academic pursuits but also has practical implications for public safety and urban planning. As seismology continues to advance, insights gained from the Chile Triple Junction are becoming invaluable in designing more resilient infrastructure and developing effective emergency response strategies to mitigate the risks posed by potential earthquakes.
Exploring Slab Window Dynamics and Their Impact on Earthquake Activity
Recent studies have revealed intricate connections between slab window dynamics and regional earthquake activity, particularly in tectonically active zones. Slab windows form when a tectonic plate is pulled apart, allowing asthenospheric material to migrate into the gap. This process not only alters the geological fabric of an area but also has significant implications for seismic behavior. In regions like the Chile Triple Junction, the presence of slab windows has been linked to modifications in subduction processes, resulting in the activation of previously dormant fault lines and an uptick in earthquake frequency.
The repercussions of these findings are substantial for earthquake forecasting and risk assessment. Researchers highlight that understanding slab window evolution can lead to predictive models that account for variations in seismic activity. Key factors influencing this relationship include the size and shape of the slab window, the properties of the overlying lithosphere, and the rate of tectonic plate movement. As scientists continue to explore these dynamics, they aim to provide clearer insights into the patterns of seismic events, potentially enhancing preparedness measures for communities situated near these geological phenomena.
Recommendations for Future Research in Coastal Tectonics and Seismic Safety
Future research in coastal tectonics, particularly regarding the Chile Triple Junction, should prioritize interdisciplinary approaches that integrate seismology with geology and oceanography. This convergence of fields could uncover vital connections between tectonic activity and marine processes, offering deeper insights into seismic hazards in coastal regions. Key areas for investigation include:
- The relationship between slab windows and seismic activity throughout the Chile Triple Junction.
- The impact of sediment dynamics on fault stability and earthquake prediction models.
- The role of climate change in altering coastal tectonic behavior.
Additionally, the development of advanced monitoring technologies is crucial for enhancing seismic safety. Implementing state-of-the-art sensors and data analysis methods will improve early warning systems and contribute to more effective disaster preparedness. Potential research initiatives could focus on:
- Real-time monitoring networks tailored to areas with high seismic risk.
- Machine learning algorithms for predictive modeling of seismic events.
- Community-engaged research that raises awareness and preparedness standards among local populations.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, the exploration of the Chile Triple Junction and the revelations brought forth by seismological studies underscore the intricate dynamics of our planet’s tectonic behavior. The discovery of the slab window offers a crucial insight into the geological processes that shape not only the Andean region but also global seismic activity. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of these tectonic interactions, the findings stand to enhance our understanding of earthquakes and their implications for communities situated along seismic fault lines. Continued collaboration and advancements in technology will undoubtedly pave the way for further breakthroughs in this vital field, reiterating the importance of vigilant monitoring and research in mitigating the risks associated with natural disasters. As we move forward, the implications of such findings remind us of the ever-changing nature of our Earth, urging us to remain informed and prepared.