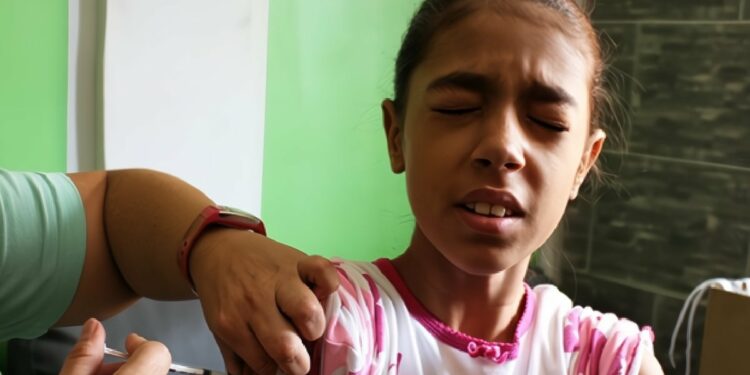
The HPV vaccine is crucial for preventing cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases, which are significant health concerns in Cuba. It also helps reduce the burden on healthcare systems by preventing costly treatments.
What age group is targeted for the HPV vaccination campaign in Cuba?
The campaign targets girls aged 9 to 10, aiming to provide early protection against HPV-related diseases.
What are the main challenges in implementing the HPV vaccination program?
Challenges include overcoming misinformation and myths about the vaccine, ensuring accessibility, and achieving high coverage levels for effective population-wide protection.
Source link : http://www.bing.com/news/apiclick.aspx?ref=FexRss&aid=&tid=67b5ad50ec194bbe8c01a86f0a229558&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cubaheadlines.com%2Farticles%2F297365&c=5378697590250504034&mkt=en-us
Author :
Publish date : 2025-02-18 19:30:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.