Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), calculated from Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data (CHIRPS) and Vegetation Health Index data from the Center for Satellite Applications and Research (STAR/NOAA).
Extreme heat and heatwaves affected central South America from August to December. Temperatures in parts of Brazil exceeded 41 °C in August as South America was hit by scorching weather in the middle of the austral winter.
Countries including Brazil, Peru, the Plurinational State of Bolivia, Paraguay and Argentina all recorded their highest September temperatures. Large wildfires burned across many of the heat-stricken regions.
The boreal summer of 2023 was exceptional for extreme heat over Mexico. Temperatures surpassing 45 °C were recorded in many stations, with a high of 51.4 °C on 29 August.
Human health, ecosystems and wildlife suffered. In Tefé Lake, in the Brazilian Amazon, water temperature reached a record high and over 150 river dolphins were reported dead.
Sea level rise is accelerating: The rate of sea level mean sea level has increased at a higher rate than the global mean in the South Atlantic and the subtropical and tropical North Atlantic. This threatens a large portion of the Latin American and Caribbean population who live in coastal areas, by contaminating freshwater aquifers, eroding shorelines, inundating low-lying areas and increasing the risks of storm surges.
Glaciers: There are approximately 4 000 glaciers in the Andes along the border between Chile and Argentina, with a smaller number in the tropical Andes. According to the World Glacier Monitoring Service (WGMS), the Echaurren Norte glacier – a reference glacier lost about 31 meters water equivalent (m w.e.) from 1975 to 2023. The retreat has accelerated this century.
Climate-related impacts and risks
According to the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT), there were 67 reported meteorological, hydrological and climate-related hazards in the region in 2023. Of these, 77% were storm- and flood-related events. The estimated USD 21 billions of economic damage reported to EMDAT was mainly due to storms (66%), including the USD 12 billions of damages associated with Hurricane Otis (data accessed 21 February 2024).
The actual amount of damage is likely to be worse because of under-reporting and because data on impacts are not available for some countries. This is especially the case for heat-related extremes.
Agriculture and food security were badly hit by ddisasters and climate change. In 2023, 13.8 million people were reported to suffer acute food crisis phase 3 or above, especially in Central America and the Caribbean.
El Niño conditions contributed to the prolonged droughts in the Central American Dry Corridor and northern South America, and to intense rainfall and flooding along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru. This hit agricultural production and exacerbated food insecurity, especially in communities reliant on agriculture for their livelihoods. The impacts will likely be felt in 2024 and beyond.
The increase of sea temperature linked to El Niño also reduced fishing catches in countries like Peru and Ecuador.
Health: The LAC region faces increased health risks due to population exposure to heatwaves, wildfire smoke, sand dust and air pollution, leading to cardiovascular and respiratory problems, as well as rising food insecurity and malnutrition.
Heatwave exposure is on the increase. According to one recent paper, this is associated with an increase in heat-related mortality of 140% from 2000-2009 and 2013-2022. In Latin America and the Caribbean, an estimated 36 695 annual heat-related excess deaths occurred between 2000 and 2019. This is likely to be an underestimate.
Air pollution, often worsened by climate change, is a serious health threat, with over 150 million people in the LAC region living in areas exceeding World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines.
Changing rainfall patterns and warming temperatures are expanding the geographic distribution of diseases such as malaria. In 2019, over 3 million cases of dengue were reported in the Americas, the highest number on record. This number was exceeded in the first 7 months of 2023.
Air pollution, often worsened by climate change, is a serious health threat, with over 150 million people in the LAC region living in areas exceeding World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines.
Changing rainfall patterns and warming temperatures are expanding the geographic distribution of diseases such as malaria. In 2019, over 3 million cases of dengue were reported in the Americas, the highest number on record. However, this number was already exceeded in the first 7 months of 2023.
Climate services are pivotal in enhancing decision-making and action in various sectors. Despite some progress, only 38% of WMO Members in the region indicated providing tailored climate products for the health sector.
However, strides are being made to increase health sector resilience to climate change. Twelve of thirty-five countries in the Americas are developing Health National Adaptation Plans. A 2021 Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) survey shows that 17 countries are integrating meteorological data into health surveillance, focusing on diseases and extreme weather impacts. This reflects a move towards stronger public health and strategies.
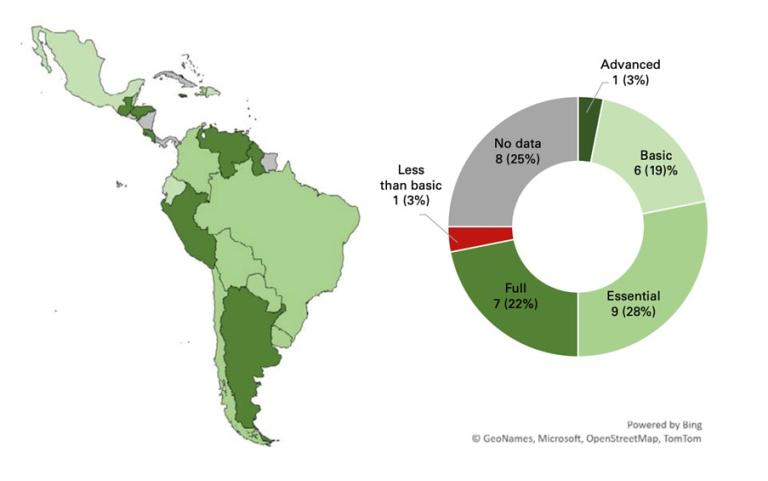
Overview of generalized climate services capacities (not sector specific). The information in the figure represents 32 WMO Members whose data have been validated by internationally certified auditors.
State of the Climate in Latin America and the Caribbean 2023 – Animation – English
Source link : https://wmo.int/news/media-centre/el-nino-and-climate-change-impacts-slam-latin-america-and-caribbean-2023
Author :
Publish date : 2024-05-08 03:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.












