exploring teh Petit-Saut Reservoir: A Key Resource in South America
In the heart of South America lies the Petit-Saut Reservoir, a crucial body of water that plays a significant role in the region’s ecological and economic landscape. Featured prominently in research and environmental studies, particularly in the work presented on ResearchGate, Fig. 12.1 offers a detailed map of the reservoir, highlighting its geographic boundaries, surrounding infrastructure, and the intricate web of biodiversity it supports. As discussions around enduring management, hydropower generation, and conservation efforts intensify globally, understanding the features and functions of the Petit-Saut Reservoir becomes increasingly essential. This article delves into the history, importance, and ongoing research surrounding this vital resource, shedding light on its multifaceted impact on the habitat and local communities alike.
Understanding the Geographic Context of the Petit-Saut Reservoir
The Petit-Saut Reservoir, situated in the heart of French Guiana, is intimately woven into the region’s ecological and socio-economic fabric. This man-made lake, formed by the damming of the Sinnamary River, spans approximately 3,200 hectares, making it a significant feature in the local landscape. Its creation not only altered the hydrology of the area but also served various purposes, including hydroelectric power generation and flood control, thus impacting the surrounding communities and ecosystems.
The geographic context of the reservoir is characterized by its tropical rainforest surroundings, rich biodiversity, and unique geological formations. The area is underpinned by the Guiana Shield, one of the oldest geological formations on Earth, providing not just natural beauty but also essential resources. Here are some key geographic features of the Petit-Saut Reservoir area:
- proximity to Major Towns: Located near the town of Sinnamary, the reservoir is a vital resource for local inhabitants.
- Floral and Faunal Diversity: The surrounding rainforest is home to a myriad of species, making it a hotspot for biodiversity.
- Hydrological Impact: The dam has transformed local water systems, creating new aquatic habitats while affecting existing ecosystems.
the reservoir’s geographic significance is further enhanced by its influence on local climate and weather patterns. The vast water body acts as a climate regulator,helping to stabilize temperatures and humidity levels in the vicinity. The interplay between the reservoir and the rainforest elevates the importance of understanding these dynamics to address challenges such as climate change and environmental sustainability. A detailed analysis of the reservoir’s geographic context reveals not just its role as a power source but also as a critical element in regional ecology and community life.

analyzing the Environmental Impact on Local Ecosystems
The environmental repercussions of the Petit-Saut reservoir are multifaceted, significantly affecting both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. In particular, the alteration of the local hydrology has led to noticeable changes in species composition and habitat functionality. as waters rise and fall within the reservoir, a range of emersed and submerged vegetation types create unique yet fragile habitats.
Among the most critical impacts are:
- Water Quality Deterioration: Increased sedimentation and nutrient runoff can lead to algal blooms, reducing oxygen availability for aquatic life.
- Habitat Alteration: The inundation of previously terrestrial ecosystems has displaced flora and fauna, requiring species to adapt, migrate, or face extinction.
- Biodiversity Loss: The introduction of invasive species during the reservoirﻗs formation has further intricate local ecological dynamics.
To assess the extent of these changes, researchers have conducted various studies, showcasing the contrasting impacts on wildlife and plant communities. The table below presents a snapshot of species affected by ecosystem disruptions caused by the reservoir’s operation:
| Species | Impact Type | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Dolphins | Declining Population | Endangered |
| Riverine Capybara | Habitat loss | Vulnerable |
| Amazonian Manatee | Feeding Grounds Altered | Near Threatened |
Ultimately, the assessment of environmental impact around the Petit-Saut reservoir highlights the delicate balance between human development and ecological preservation. Understanding these effects is crucial for implementing measures that promote sustainable practices, ensuring both the reservoir’s utility and the conservation of its surrounding biodiversity.

Hydrological Dynamics: Water Management Strategies in Focus
The Petit-Saut reservoir, nestled in South America, serves as a critical case study for understanding hydrological dynamics and implementing effective water management strategies. This man-made reservoir not only provides essential resources but also highlights the need for balancing ecological health with human demands.
Effective water management strategies in the region can include:
- Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM): A extensive approach that considers the interconnectedness of water and ecosystems.
- Environmental Flow Assessment: establishing minimum water flows to support aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes to ensure sustainable practices and equitable access to water resources.
Monitoring and adaptive management are also crucial elements in optimizing the reservoir’s performance. The following table highlights some of the key indicators for evaluating the effectiveness of water management strategies:
| Indicator | Objective | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Water Quality | Ensure safe drinking and aquatic life | Monthly |
| Water Levels | Maintain optimal reservoir capacity | Weekly |
| Ecosystem Health | Assess biodiversity and habitat stability | Quarterly |
| Community Satisfaction | Gauge local support for management practices | Annually |
Through the integration of innovative strategies and continuous assessment, the Petit-Saut reservoir can evolve into a model for sustainable water management in diverse ecological contexts.
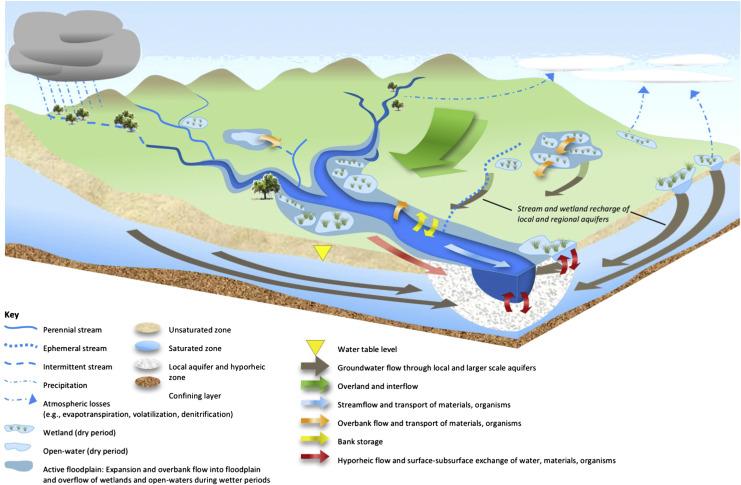
Sustainable Development Opportunities Surrounding the Reservoir
The Petit-Saut reservoir presents a canvas for sustainable development opportunities that can benefit both the local ecosystem and the surrounding communities. By leveraging its natural resources wisely, stakeholders can foster a symbiotic relationship between environmental conservation and economic growth. Here are several areas where sustainable initiatives can be implemented:
- Eco-Tourism: Developing eco-friendly tourism activities, such as guided nature walks, bird watching, and canoe tours, can promote environmental awareness while generating income for local communities.
- renewable Energy Projects: The reservoir can serve as a foundation for renewable energy initiatives, particularly in solar and wind energy, harnessing natural resources to support sustainable energy production.
- Aquaculture Practices: Implementing sustainable aquaculture techniques can enhance fish populations without degrading water quality, providing both a food source and economic opportunities for local fishermen.
- environmental Education Programs: Establishing programs that educate the community and visitors about the importance of the reservoir’s ecosystem can foster a culture of conservation.
Along with these initiatives, collaboration between governmental bodies, non-profit organizations, and local communities is essential for the prosperous implementation of projects. The following table outlines potential stakeholders and their roles:
| Stakeholder | Potential Role |
|---|---|
| Local goverment | Policy formulation and funding support |
| Non-Profit Organizations | Project management and community engagement |
| Local Residents | Participating in initiatives and providing feedback |
| Businesses | Supporting sustainable practices and local economy |
By capitalizing on these sustainable development opportunities, the Petit-Saut reservoir can morph into a model for ecological preservation and community empowerment. The careful balancing of environmental health with economic viability has the potential to create a thriving ecosystem that benefits all stakeholders involved.

Future Research Directions and Policy Recommendations
The Petit-Saut reservoir presents a unique case study for future environmental and social research initiatives. As the dynamics of such a large water body interact with the surrounding ecosystems and communities, key areas warrant further investigation:
- Ecosystem Resilience: Studies shoudl focus on the biodiversity within the reservoir and assess how species adapt to changes in water levels.
- Community Engagement: Research on how local communities interact with the reservoir can help develop effective engagement strategies and ensure that their needs are met.
- Climate Change Impact: Evaluating how climate variations affect the reservoir’s hydrology and its subsequent effects on local wildlife and human activities is crucial.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Long-term studies aimed at monitoring and managing water quality will provide insights on pollution trends and help guide policy adjustments.
To complement these research directions, specific policy recommendations can enhance conservation efforts and community welfare:
| Policy Area | recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Water Resource Management | Implement adaptive management strategies that respond to ecological monitoring. |
| Community Involvement | develop programs that actively involve local communities in conservation efforts. |
| Research Funding | allocate specific funds for research projects that focus on sustainability in and around the reservoir. |
| Pollution Control | Enforce stricter regulations on effluent discharge into water bodies. |
By actively pursuing these research avenues and implementing sound policy recommendations, stakeholders can foster a sustainable balance between human activity and natural preservation at the petit-Saut reservoir. The collaboration among researchers,policymakers,and the local population will be essential in ensuring that the reservoir continues to thrive as a vital ecological and social asset.

Final Thoughts
Fig. 12.1 serves as a crucial visual tool that encapsulates the geographic and environmental nuances surrounding the Petit-saut reservoir in South America. This map not only provides stakeholders with essential data about the reservoir’s location and its surrounding features, but it also highlights the complex interplay between natural resources and human activity in the region. As research progresses, continued emphasis on mapping and data visualization will be essential in facilitating sustainable management practices. The Petit-Saut reservoir, thus, remains a significant focal point for further studies, underscoring the ongoing need for informed decision-making that harmonizes ecological preservation with developmental goals. As we look ahead,the insights gleaned from such studies will be vital in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change and resource management in the Amazon basin and beyond.












