Exploring Dengue Fever: Insights from the CDC on High-Risk Regions
Dengue fever remains a significant health concern in numerous parts of the world, making public awareness and proactive strategies more essential than ever.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has taken the lead in monitoring and educating communities about areas with an elevated risk of dengue transmission. This article examines the CDC’s recent insights, highlighting critical geographical hotspots for dengue, factors that contribute to outbreaks, and essential measures individuals can adopt to safeguard their health. With an increase in dengue cases globally, it is imperative to remain vigilant and informed.
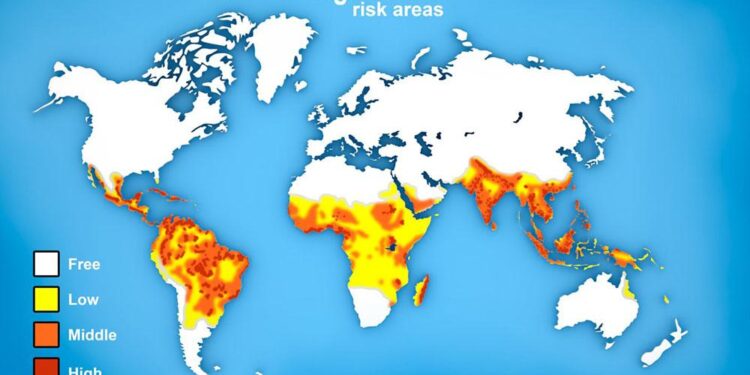
Dengue Risk Areas in the United States
Dengue fever is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes that has been increasingly reported in regions once deemed safe from this illness. Recognizing these risk areas within the United States is crucial for public health initiatives. The primary culprits behind dengue transmission are Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, which flourish in warm, humid environments.Recent climate changes coupled with urban expansion have allowed these mosquito species to spread into new territories,heightening the potential for outbreaks.
The latest statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) categorize various U.S. regions based on historical transmission patterns alongside current mosquito populations:
- High Risk: Areas experiencing frequent outbreaks; predominantly found in southern states like Florida and Texas.
- Moderate Risk: Regions with sporadic cases; includes parts of California and Arizona.
- Low Risk: States that seldom report dengue incidents; typically located in northern regions such as Illinois or New York.
| Risk Level | Select States | Causative Factors | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Risk | Tennessee, Louisiana | Mild climate conducive to mosquito breeding. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moderate Risk | Nevada, New Mexico | Isolated incidents due to environmental shifts. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Low Risk | Maine, North Dakota | Harsh winters limit mosquito survival.
Strategies to Prevent Dengue Spread in High-Risk RegionsDengue fever represents a serious health challenge especially during wet seasons when stagnant water provides ideal breeding conditions for mosquitoes. To curb virus transmission effectively, communities must adopt a multifaceted approach combining individual actions with community involvement.Key strategies include:
Beyond personal responsibility , public health campaigns are vital components of reducing dengue spread . Local authorities should prioritize educational outreach through awareness programs . Effective initiatives may encompass :
Together , these individual efforts combined with collective action can considerably lower risks associated with dengue while enhancing overall public safety . Â The Importance of Community Engagement Against Dengue TransmissionAn informed community plays an integral role when it comes down combating diseases like dengue which pose considerable threats across many locales . By grasping how this illness spreads along with its symptoms , residents become empowered participants within preventive measures especially prevalent where endemicity exists . Essential actions include :</ p
Additionally , collaborative partnerships between healthcare providers & local citizens amplify awareness while driving effective responses towards disease control efforts . By establishing alliances , municipalities can deploy dialog strategies reaching diverse demographics through various channels including media campaigns workshops schools etc.. Below outlines prosperous community-driven projects : Â
|