#4. Microsoft allocates close to $1 billion annually to cyber security initiatives
Amidst the challenges of the digital era, Microsoft remains vigilant against modern cyber security threats, with this significant investment indicative of their commitment. This sum does not include additional expenses on acquiring companies in the cyber security sector.
#5. Small firms typically invest less than USD 500 in cyber security on average
Given their cautious approach, small firms often opt for consumer-grade security services, accounting for 13% of the cyber security market. Statistics reveal that small businesses are attractive targets for cyber criminals due to their lower investment in cyber securityﻗﻗ.
#6. JPMorgan Chase dedicates approximately USD 600 million annually to cyber security services
With over 3,000 personnel in the cyber security unit, JPMorgan has boosted its yearly cyber security budget by an additional 100 millionﻗﻗ.
#7. A third of US companies have invested in liability or cyber data breach insurance
Specialized insurance provisions enable companies to recuperate losses in case cybersecurity solutions are compromised, with 68% of firms lacking such coverage and 25% considering investment, as per cyber security statisticsﻗﻗ.
#8. Projected growth for the Cyber Insurance market surpasses $20 billion in the next three years
Anticipated expansion in the cyber insurance sector expects to exceed $20 billion within five years, with US-based firms poised to drive most of this growthﻗﻗ.
#9. Companies allocate up to USD 500,000 to probe their systems by hackers
Known as ﻗWhite Hatﻗ hackers, these individuals leverage their skills for ethical purposes, aiding companies like Tesla in fortifying their security systemsﻗﻗ.
Cyber Crime Statistics
#9. 1 out of 10 small firms fall victim to a cyber attack annually
The vulnerability of small businesses to cyber attacks highlights the need for increased cyber security investment to safeguard against cyber criminal activitiesﻗﻗ.
#10. Ransomware attacks occur every 14 seconds
Ransomware, a lucrative form of malware, is currently prevalent, with attacks surging in frequencyﻗﻗ.
#11. A cyber attack occurs every 39 seconds
Unsecured systems connected to the internet face a daily barrage of over 2,000 cyber attacks, driven by automated tools and scripts utilized by hackers to exploit vulnerabilitiesﻗﻗ.

(According to Cybersecurity Ventures)
#12. Only 10% of cyber crimes are reported in the US
Despite hosting numerous tech giants, the US reports only a fraction of cyber crimes, often due to the challenges of substantiating such incidentsﻗﻗ.
#13. Predictions suggest that over 50% of future cyber crime attacks will target the US by 2027
Forecasts indicate a substantial increase in cyber crime targeting the US, underscoring the nationﻗs vulnerability to cyber attacksﻗﻗ.
US-based companies should reinforce their protection against cyber threats due to the projected increase in cyber crime attacks within the next five years.
#14. A hospital in Germany reported the first death caused by a ransomware attack
In September 2020, the initial documented death from a ransomware attack occurred during an IT failure linked to ransomware at a hospital in Dusseldorf, Germany.
#15. Phishing accounts for more than 90% of successful cyber attacks targeting trades
Recent cyber security statistics reveal that phishing remains a prevalent form of cyber attack, leveraging human nature for its success.

#16. Phishing contributes to 37% of all cyber crime attacks on businesses
Phishing leads more than a third of the cybercrime attacks faced by organizations.
#17. Bitcoin is involved in illegal activities totaling USD 76 billion annually
Despite Bitcoinﻗs popularity as a cryptocurrency, it has been linked to cyber violence and unlawful activities due to its inherent anonymity in transactions.
#18. The largest DDoS attack involved the transfer of 1.3 TB of data per second
In 2018, the software depository platform GitHub experienced an immense DDoS attack where cyber criminals transferred approximately 1.3 TB of data every second.
#19. Financial motives drive most data breaches
Data breaches predominantly target credentials as the most sought-after data type, followed closely by personal information.
#20. DDoS attacks have increased by 39% compared to the previous year
Recent cyber security statistics indicate a significant rise in DDoS attacks, with cyber criminals utilizing them more frequently, particularly targeting satellite and wireless communication companies.
#21. Cyber criminals can obtain their tools for as low as USD 1
Hackers have access to basic malware kits for just $1, and other hacking tools such as compromised emails or passwords for minimal costs.
#22. A human element is responsible for 85% of data breaches
#23. During data breaches, external cloud data are more vulnerable compared to on-premise assets.
Cyber Crime Cost And Damage Statistics
#24. Predictions suggest that cyber crimes will cause an annual damage of USD 10.5 trillion by 2025
The anticipated annual damage from cyber crime attacks is projected to reach $6 trillion in 2022, with already recorded damages of USD 2 trillion due to cyber security threats.

(According to Cybersecurity Ventures)
#25. Companies lose an average of USD 188400 per year due to cyber crime attacks
Businesses, both large and small, endure significant time and financial losses combating cyber crime attacks, with about 97% of small enterprises able to recover costs due to cyber insurance.
#26. US-based companies demonstrate a reluctance to pay ransom amounts to hackers
Many US companies adhere to the policy of not negotiating with cyber terrorists, as shown by only 3% of US-based firms paying ransoms to cyber criminals.
#27. FedEx suffered USD 300 million in damages following a ransomware attack
After a cyber security breach, FedExﻗs stock value plummeted by 79% per share.
#28. Atlanta incurred around USD 17 million in recovery costs after falling victim to a ransomware attack
When targeted by SamSam ransomware, the city of Atlanta faced escalating recovery expenses due to compromised data, including valuable city programs and police records.
#29. The healthcare industry is projected to invest USD 125 billion in cyber security services from 2020 to 2025
In 2018, the healthcare sector was particularly targeted by ransomware attacks, reflecting the increased frequency of cyber attacks on healthcare entities.
#30. Formjacking attacks lead to monthly damages of USD 2.2 million
Approximately 4800 websites fall victim to formjacking attacks each month, enabling cyber criminals to harvest user data like credit card details and login credentials.
#31. 47% of cybercrime victims suffer financial losses after experiencing cyber attacks, according to cybersecurity stats.
#32. In 2021, victims with infected business and personal email accounts incurred losses amounting to USD 1.86 billion.
Data Breach Statistics And Facts
#33. Experts estimate that the average cost of a data breach in 2021 was USD 13 million
Despite the growing investments in cyber insurance, cyber breaches are expected to rise in the upcoming years.
#34. The largest data breach compromised 3 billion user accounts in history
In 2017, Yahoo faced a monumental data breach, marking it as the most significant security breach incident to date.
#35. Facebook experienced a recent security breach as well
In 2019, Facebook encountered a substantial security breach, exposing account information such as names, comments, user IDs, and reactions to the public.
The security breach has led to the exposure of around 600 million FB accounts, which were stored in plain text files.
#36. Cybersecurity statistics indicate that 95 user credentials are stolen every second.
Annually, more than 3 billion passwords and credentials get compromised or stolen, either through data breaches or malware. E-banking services now require regular password updates. It is recommended by experts to have unique passwords for each website or application.
Facts About Cyber Security
#37. Following a VPN attack in April 2021, the US Colonial Pipeline paid hackers $5 million in Bitcoin.
This incident affected the companyﻗs multi-factor authentication system.
#38. Spam has emerged as the most prevalent cyber threat exploiting the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Spam emails were responsible for 65.7% of online threats associated with the COVID-19 crisis.
#39. In comparison to pre-COVID times, 44% of adults felt more susceptible to cyber attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Due to the lifestyle changes brought about by the pandemic, almost two out of five adults took steps to safeguard their online activities and personal information.
#40. Since the onset of COVID-19, the FBI observed a 300% surge in reported cybercrime attacks.
These attacks, which included ransomware demands for cryptocurrency payments, multiplied significantly.
#41. A majority of firms express doubts about their adequate protection against cybercrime attacks.
According to a survey, more than half of the surveyed firms harbor concerns about the security of their data. Most firms believe they need more robust defenses against cyber attacks.
#42. Despite heightened security concerns, the most commonly used password is ﻗ123456ﻗ.
Common and easily guessed passwords continue to pose significant cybersecurity risks as revealed by cyber security facts.
#43. Besides financial repercussions, a cybercrime attack can tarnish a companyﻗs reputation.
Cyber attacks not only impact a companyﻗs public image but also affect its employees and clients through data breaches.
#44. Nearly 58% of firms have over 100,000 unprotected folders.
Network firewalls serve as the primary line of defense. If companies extend protection to additional folders, hackers would find it harder to breach their systems. However, approximately 60% of firms remain vulnerable due to inadequately protected folders.
#45. Every third user account is classified as a stale account.
Even after an employee leaves the company, their account often remains active for a prolonged period, known as a stale account. Such accounts serve as potential entry points for cyber criminals.
#46. More than 40% of firms house over 1,000 unprotected sensitive files on their servers.
Many companies have not adequately secured sensitive files such as health records, credit card numbers, and Social Security numbers, posing a significant security risk.
#47. Only 20% of people in the US change their passwords after learning about hacking incidents reported in the news.
Most individuals only change their passwords when prompted or when they face difficulty remembering them. Merely one-fifth of individuals in the US update their passwords following news reports of security breaches.
#48. More than 60% of firms maintain more than 1,000 stale user accounts.
Retaining thousands of obsolete user accounts can pose risks for companies.
#49. IoT devices can be compromised within minutes of connecting to the internet.
Contrary to popular belief, IoT devices such as smart TVs, cars, speakers, and thermostats are vulnerable to cyber attacks. These devices lack integrated protection, making network firewalls the most effective defense.
#50. Users should refrain from using third-party app stores to ensure a malware-free smartphone.
Human error remains a prevalent cause of security breaches. Users are advised to exclusively use apps from manufacturers to safeguard their smartphones against hackers.
#51. There exist five types of cyber security measures.
Securing critical infrastructure, network, cloud, applications, and IoT devices are among the five categories of cybersecurity.
#52. 53% of adults believe that remote work has provided cyber criminals and hackers with an advantage.
#53. Proper defense against hackers is also essential for cloud-based storage and apps.
Recent Happenings
AnyDesk Cyber Attack: AnyDesk, a remote desktop software company, faced a cyber attack compromising its production systems. As a precautionary measure, all security-related certificates and web portal passwords were revoked.
Russian APT28 Hackers Targeting: The state-sponsored group, APT28, has been launching NTLM Relay Attacks targeting organizations globally in sectors like foreign affairs, energy, defense, and transportation.
DirtyMoe Malware in Ukraine: Over 2,000 Ukrainian computers fell victim to the DirtyMoe malware, capable of executing cryptojacking and DDoS attacks.
Cloudflare Breach: Cloudflare disclosed a breach by likely nation-state actors who accessed some documentation and a limited amount of source code.
US Sanctions Iranian Officials: In response to cyberattacks against an Israeli PLC vendor, the US government sanctioned six Iranian government officials.
Layoffs at Security Vendors: Okta and Proofpoint announced layoffs impacting nearly 1,000 employees in the US and Israel.
Clorox Cyberattack Costs: Clorox reported that a cyberattack has incurred over $49 million in costs so far, with additional expenses projected for 2024.
Conclusion
Cyber security continues to evolve rapidly in 2024, driven by technological advancements and cyber criminalsﻗ increasing sophistication. Reports from the World Economic Forumﻗs Global Cyber security Outlook and other authoritative sources indicate that while the number of credential leaks remains stable, cyber criminals are now resorting to more sophisticated methods to acquire them, with a considerable portion of these credentials originating from corporate sources.
This underscores the critical importance of implementing robust corporate cyber security measures to counter such threats. Moreover, the complexity of attacks is on the rise, with ransomware groups adopting advanced strategies and targeting specific industries based on vulnerabilities and potential ransom amounts. This shift towards more targeted and financially motivated cybercrimes emphasizes the urgent need for organizations to strengthen their defenses and adopt proactive security measures.
The statistics paint a picture of a digital landscape where no sector remains untouched, and the global cost of cyber crime is expected to be substantial. The United States bears the brunt of data breachesﻗ costs, underscoring the necessity of increased investments in cyber security measures. In response to these challenges, the trend toward leveraging artificial intelligence for threat intelligence and automation is gaining traction, presenting a promising avenue for enhancing organizational security postures.
As cyber threats grow in complexity, comprehensive monitoring and swift action are becoming increasingly critical.The importance of response and the adoption of AI-driven technologies in cybersecurity cannot be emphasized enough. Organizations must give priority to these strategies to effectively navigate the complexities of the current cyber security landscape and ensure resilience against the ever-evolving threats.
[3px] border-t-[3px] p-4 border-[#1d598f] my-4″ style=”box-shadow: 0 0 14px rgb(9 38 66 / 8%);”>
Sources
How many cyber attacks occurred in the US last year?
Around 2000 cybercrime complaints were reported in the US in 2021.
Cyber Security Statistics 2024 Facts and Trends That Users Need To Know
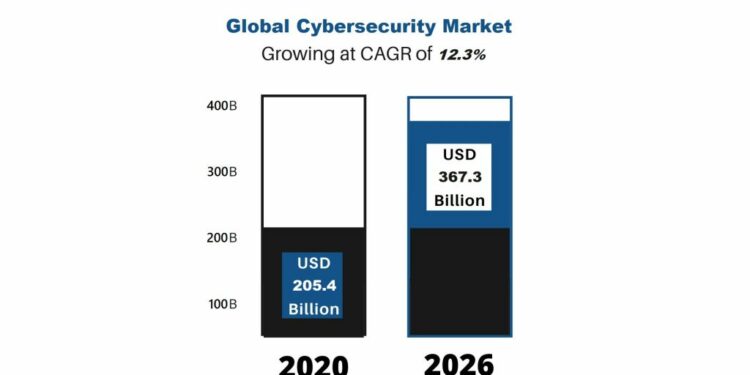
Data is from 2023 and 2024, and forecast data is for 2025 and 2026. The forecast data has been extended to include 2027 and 2028.
——
REFERENCES:
This information was taken from various sources around the world, including these countries:
Australia, Canada, USA, UK, UAE, India, Pakistan, Philippines, Indonesia, Nigeria, Tanzania, Kenya, US, United Kingdom, United States of America, Malaysia, U.S., South Africa, New Zealand, Turkey, United Arab Emirates.
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, American Samoa, Andorra, Angola, Anguilla, Antarctica, Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Armenia, Aruba, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan.
Bahamas, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Barbados, Belarus, Belgium, Belize, Benin, Bermuda, Bhutan, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Botswana, Bouvet Island, Brazil, British Indian Ocean Territory, Brunei Darussalam, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Burundi.
Cambodia, Cameroon, Canada, Cape Verde, Cayman Islands, Central African Republic, Chad, Chile, China, Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling Islands), Colombia, Comoros, Congo, Cook Islands, Costa Rica, Cote DﻗIvoire (Ivory Coast), Croatia (Hrvatska), Cuba, Cyprus, Czech Republic.
Denmark, Djibouti, Dominica, Dominican Republic, East Timor, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Estonia, Ethiopia, Falkland Islands (Malvinas), Faroe Islands, Fiji, Finland, France, Metropolitan, French Guiana, French Polynesia, French Southern Territories.
Gabon, Gambia, Georgia, Germany, Ghana, Gibraltar, Greece, Greenland, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Guam, Guatemala, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Guyana, Haiti, Heard and McDonald Islands, Honduras, Hong Kong, Hungary, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Israel, Italy.
Jamaica, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kiribati, North Korea, South Korea, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Latvia, Lebanon, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg.
Macau, Macedonia, Madagascar, Malawi, Malaysia, Maldives, Mali, Malta, Marshall Islands, Martinique, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mayotte, Mexico, Micronesia, Moldova, Monaco, Mongolia, Montserrat, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar.
Namibia, Nauru, Nepal, Netherlands, Netherlands Antilles, New Caledonia, New Zealand (NZ), Nicaragua, Niger, Nigeria, Niue, Norfolk Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Norway.
Oman, Pakistan, Palau, Panama, Papua New Guinea, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Pitcairn, Poland, Portugal, Puerto Rico, Qatar, Reunion, Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and The Grenadines, Samoa, San Marino, Sao Tome and Principe.
Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Serbia, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, Solomon Islands, Somalia, South Africa, South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands, Spain, Sri Lanka, St. Helena, St. Pierre and Miquelon, Sudan, Suriname, Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands, Swaziland, Sweden, Switzerland, Syria.
Taiwan, Tajikistan, Tanzania, Thailand, Togo, Tokelau, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Turks and Caicos Islands, Tuvalu, Uganda, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates (UAE), UK (United Kingdom), USA (United States of America, U.S.), US Minor Outlying Islands.
Uruguay, Uzbekistan, Vanuatu, Vatican City State (Holy See), Venezuela, Vietnam, Virgin Islands (British), Virgin Islands (US), Wallis and Futuna Islands, Western Sahara, Yemen, Yugoslavia, Zaire, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
Cyber Security Statistics 2024 Facts and Trends That Users Need To Know
August 29, 2024
Source link : http://www.bing.com/news/apiclick.aspx?ref=FexRss&aid=&tid=66d7c25b278e4bcf973ce1c248b22815&url=https%3A%2F%2Fhollywoodgazette.com%2Fcybersecurity-statistics-html%2F&c=13009930206896571979&mkt=en-us
Author :
Publish date : 2024-09-03 13:53:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.