As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding the genetic diversity of the virus remains crucial in the fight against its spread and the emergence of new variants. A recent study published in Nature sheds light on the intricate tapestry of SARS-CoV-2 variants that have circulated in Nicaragua throughout the pandemic. This research not only elucidates the evolutionary trajectory of the virus in a Central American context but also underscores the importance of genomic surveillance in informing public health strategies. By meticulously tracking the genetic variations of SARS-CoV-2 within Nicaragua, scientists aim to enhance our understanding of how such variants might influence transmissibility, vaccine efficacy, and the potential for future outbreaks. As new variants continue to emerge worldwide, this focused analysis provides valuable insights into a region that has faced unique challenges during the COVID-19 crisis.
Understanding the Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Nicaragua Amid the Pandemic
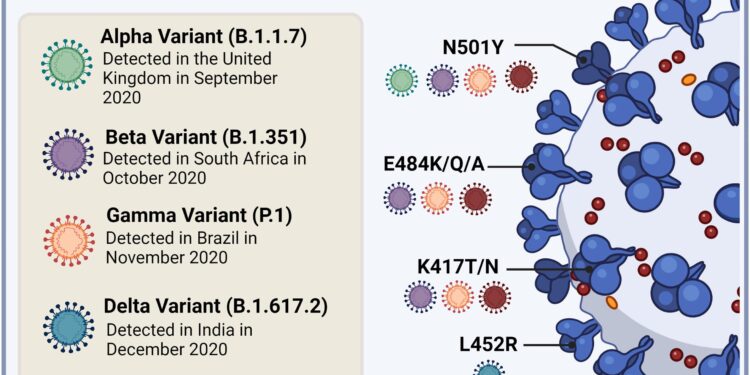
The emergence and proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Nicaragua has significantly shaped the trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic within the country. Genetic sequencing efforts have unveiled a complex landscape of viral mutations, reflecting the adaptive nature of the virus. Key variants identified in Nicaragua include:
- Alpha variant: First detected in late 2020, known for its increased transmissibility.
- Delta variant: Dominated in mid-2021, associated with severe illness and hospitalizations.
- Omicron variant: Emerged late 2021, displaying a diverse array of subvariants that are currently circulating.
As researchers continue to monitor these variants, it is crucial to understand their implications on public health and vaccination strategies. Ongoing genomic surveillance will play a vital role in tracking variant prevalence and potential resistance to therapeutics. Data analysis reveals a concerning trend of increased mutation rates, which may affect vaccine efficacy and therapeutic interventions. The table below summarizes the key characteristics of the predominant variants in Nicaragua:
| Variant | First Identified | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha | December 2020 | Higher transmissibility |
| Delta | April 2021 | Increased hospitalizations |
| Omicron | November 2021 | Diverse sublineages |
Assessing the Impact of Genetic Diversity on Public Health Strategies in Nicaragua
The study of genetic diversity among SARS-CoV-2 variants in Nicaragua has unveiled critical insights that could reshape public health strategies in the region. By identifying and tracing the evolution of various variants, researchers have highlighted key patterns in transmission and mutation rates. This understanding can lead to enhanced monitoring efforts and inform vaccination campaigns tailored to the most prevalent strains. Important findings suggest that areas with higher genetic diversity may experience increased transmission dynamics, necessitating focused interventions. Below are notable observations from the research:
- Mutation Rates: Increased mutations were documented in regions with high transmission rates.
- Vaccine Efficacy: Some variants showed resistance to current vaccines, raising concerns for public health initiatives.
- Community Impact: Variants linked to community spread have resulted in targeted health messaging and localized response plans.
Moreover, the findings also indicate potential demographic factors influencing variant spread, such as age and socio-economic status. Policymakers must consider these factors to prioritize vaccine accessibility in the most affected populations. To illustrate the correlation between variant prevalence and socio-economic factors, the following table summarizes key data from the research:
| Variant | Prevalence (%) | Socio-Economic Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| B.1.1.7 | 45 | High |
| B.1.617.2 | 30 | Medium |
| Alpha | 15 | Low |
This data underscores the necessity for adaptive public health strategies that leverage genetic insights to combat the evolving threat posed by SARS-CoV-2 variants in Nicaragua. As the pandemic continues to unfold, ongoing genetic tracking will be vital in shaping a responsive, evidence-based health framework.
Recommendations for Enhanced Surveillance and Response to Future Virus Variants
In light of the evolving nature of SARS-CoV-2 variants, it is crucial for health authorities in Nicaragua to prioritize enhanced surveillance systems. This can be achieved by implementing a comprehensive multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Strengthened genetic sequencing: Expanding the capacity for whole-genome sequencing across various regions to ensure rapid identification of new variants.
- Real-time data sharing: Establishing a centralized platform for sharing genomic and epidemiological data to facilitate prompt responses across governmental and health organizations.
- Community engagement: Involving local communities in reporting symptoms and testing data to enhance grassroots surveillance efforts.
Moreover, proactive measures must be taken to develop a robust response framework that addresses the potential impact of emerging variants. Consideration should be given to:
- Adaptive vaccination strategies: Tailoring immunization campaigns based on the genetic profiles of prevalent variants to improve vaccine effectiveness.
- Preparedness training: Conducting regular training for healthcare professionals to recognize and respond to novel variants quickly.
- Collaborative research initiatives: Partnering with international health organizations to stay informed on global trends in viral mutation and spread.
Final Thoughts
As Nicaragua continues to navigate the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic, the tracking of SARS-CoV-2 variants has emerged as a crucial component in understanding and responding to this ever-evolving crisis. The comprehensive study published in Nature highlights not only the genetic diversity of the virus across different regions of the country but also underscores the importance of genomic surveillance in informing public health strategies.
With the ongoing challenges posed by new variants, the findings serve as a call to action for policymakers, researchers, and healthcare professionals alike. Enhanced surveillance efforts could prove vital in controlling outbreaks and tailoring vaccination campaigns to maximize their effectiveness. As Nicaragua moves forward, the insights gained from this research may pave the way for more resilient public health responses, ensuring that the lessons learned during the pandemic are not forgotten.
In a world where infectious diseases can spread rapidly across borders, the commitment to understanding the genetic makeup of pathogens like SARS-CoV-2 will be fundamental in safeguarding not just Nicaraguans, but global health as a whole. The implications of this research extend far beyond pandemic response, informing future mobilization against emerging infectious threats that lie on the horizon.