As wildfires sweep across south America, the devastating impact of climate change has taken center stage, illuminating the urgent need for global action. The Guardian’s latest report, “The Earth is crying out for help: as fires decimate South America, smoke shrouds its skies,” offers a sobering glimpse into the environmental crisis that has led to the destruction of vast areas of forest, wildlife habitat, and indigenous lands. With the air thickened by acrid smoke and the continent’s ecosystems under threat, this article delves into the causes of the recent surge in fires, the dire consequences for both the surroundings and local communities, and the broader implications for our planet. As visuals of choked skies and charred landscapes emerge, the outcry for intervention grows louder, underscoring the critical need for collective responsibility in addressing this looming catastrophe.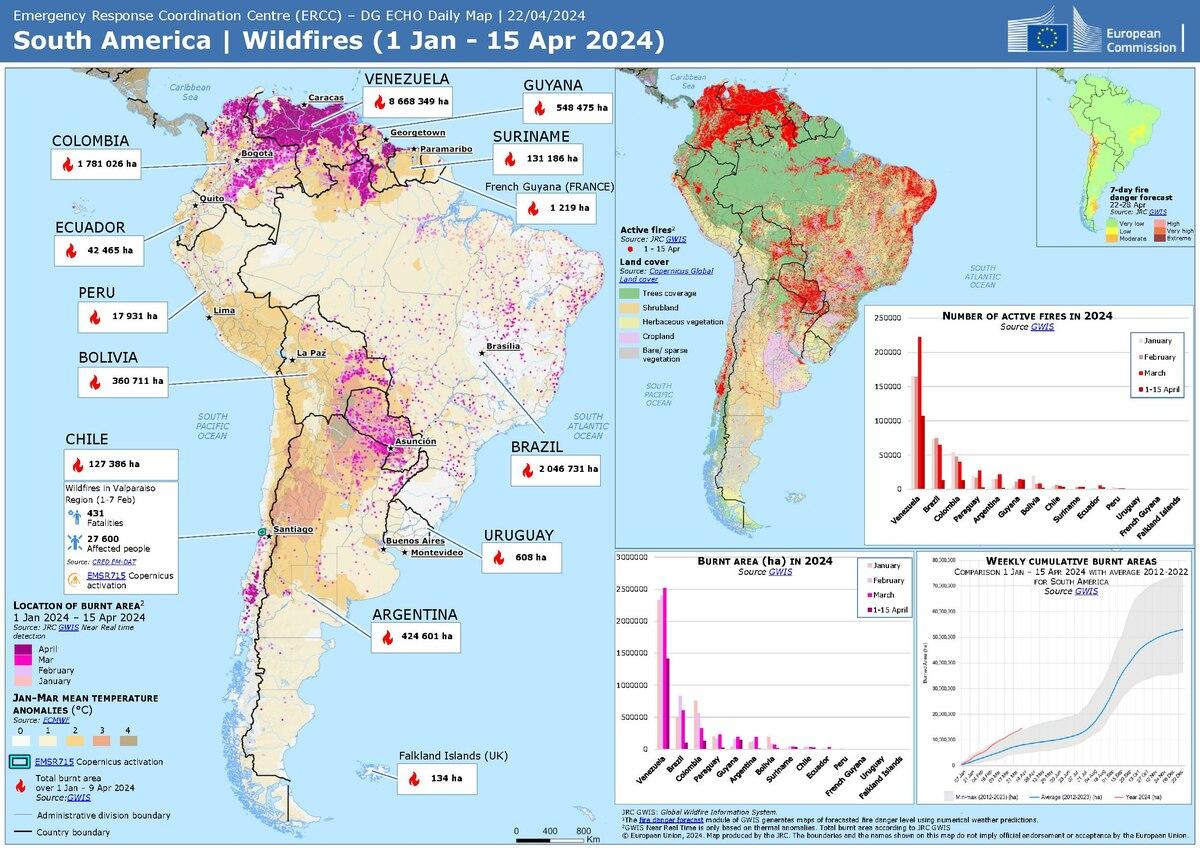
Impact of Wildfires on Biodiversity and Ecosystems in South America
The recent surge of wildfires across South America presents a devastating threat to its rich biodiversity and complex ecosystems. Forests, wetlands, and grasslands, each serving as critical habitats for countless species, are vulnerable to rapid and irreversible change.The frequency and intensity of these fires have drastically increased, leading to:
- Loss of Species: Numerous flora and fauna are put at risk as habitats are destroyed, resulting in population declines and potential extinctions.
- Disruption of Ecosystem Services: Ecosystems provide essential services, such as clean water, carbon storage, and soil fertility. Fires compromise these functions, affecting agriculture and human health.
- Altered Climate Conditions: The release of large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere exacerbates climate change,further impacting biodiversity.
One of the most affected regions is the Amazon rainforest,ofen referred to as the “lungs of the planet.” The interconnectedness of this ecosystem means that the repercussions of its destruction ripple outwards,affecting not just local wildlife but also global atmospheric conditions. Key impacts include:
| Impact | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Habitat loss for countless species |
| Soil Degradation | Reduced agricultural productivity |
| increased Erosion | Destabilization of land and waterways |
Additionally, indigenous communities who depend on these ecosystems for their livelihoods face exacerbated challenges. The loss of traditional lands not only threatens their cultural heritage but also their ability to sustain themselves. As fire continues to ravage the landscape, the urgent need for conservation efforts and enduring land management becomes increasingly paramount.
Health Risks and Environmental Consequences of Smoke Pollution
Smoke pollution poses significant health risks to individuals exposed to it, particularly vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions. Exposure to fine particulate matter, commonly found in smoke, can lead to a range of health issues, including:
- Respiratory problems: Increased incidence of asthma attacks, chronic bronchitis, and other lung diseases.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Higher risk of heart attacks and strokes due to inflammation and reduced oxygen supply.
- Neurological impacts: Potential links to cognitive impairments and other neurological disorders observed in long-term exposure.
Beyond human health, smoke pollution significantly affects the environment, exacerbating climate change and diminishing air quality.The ongoing fires across South America release vast amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to:
- Global warming: An accumulation of greenhouse gases accelerates climate change, leading to extreme weather patterns.
- Loss of biodiversity: Destruction of habitats affects countless species, pushing them closer to extinction.
- Soil degradation: When forests burn,the soil’s nutrient content is compromised,impacting agriculture and local ecosystems.
To quantify the smoke’s environmental impact, consider the following table:
| Impact Category | Effects |
|---|---|
| Air Quality | Decreased visibility, increased respiratory illnesses |
| Climate Change | increased global temperatures, erratic weather patterns |
| Biodiversity | Habitat loss, extinction of species |
| Soil Health | Loss of nutrients, increased erosion |
Government and Policy Responses: A Call for Urgent Action
The devastating wildfires engulfing South america have revealed a dire need for concerted government action and robust policy reforms. As communities brace for more damage, it becomes imperative for national and local governments to implement strategies that address this escalating crisis. Urgent measures are essential, including:
- Strengthening regulations on land use and resource extraction to prevent environmentally destructive practices that contribute to wildfire risks.
- Enhancing firefighting resources and training for local teams to ensure rapid response capabilities when blazes ignite.
- Investing in community education programs aimed at fire prevention and awareness,particularly in vulnerable rural areas.
- Promoting reforestation and sustainable agriculture as long-term solutions to restore ecological balance and mitigate future fires.
Moreover, international cooperation plays a crucial role in combating the effects of these wildfires. countries within South America must work collaboratively to share resources and knowledge, while also seeking assistance from global allies. The establishment of a dedicated climate response fund could provide necessary financial support for nations hardest hit by environmental disasters. This fund should aim to:
| Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Response | Facilitate swift mobilization of firefighting resources and personnel. |
| Restoration Projects | Fund initiatives for reforestation and habitat recovery in fire-impacted areas. |
| Training Programs | Offer skills development for local communities in fire management and prevention. |
Ultimately, the current crisis serves as a grave reminder of our shared responsibility towards environmental stewardship. Governments must act swiftly to implement transformative policies aimed not just at mitigating fires but also at addressing the broader issues of climate change and habitat degradation. The moment for decisive action is now, as the scars of these fires will linger for years to come, impacting ecosystems and livelihoods across the region.
Community Resilience: How Local Populations are Coping with Crisis
In the face of catastrophic wildfire seasons, communities across South America are stepping up to shield themselves from devastation. As flames ravage vast areas of land, the resilience of local populations has shone through; many are adapting their strategies and forming support networks to endure the mounting pressures of climate change.Innovative approaches are emerging as communities unite to tackle these crises head-on.
- Community Meetings: Grassroots organizations are convening local gatherings to share details about fire safety and emergency response.
- Volunteer Efforts: Residents are mobilizing by organizing volunteer groups to assist in firefighting and recovery efforts.
- Resource Sharing: Neighboring towns are coordinating to share resources such as fire-fighting equipment and shelters for displaced families.
Furthermore, many areas are embracing traditional knowledge and practices that have long been effective against wildfires. Indigenous practices, which often prioritize sustainable land management and biodiversity, are being revisited and integrated into modern firefighting efforts. initiatives to educate younger generations about these practices are gaining momentum, ensuring that the wisdom of the past informs current responses to crises.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Firebreaks | Creating barriers to stop the spread of fire. |
| Community Drills | Regularly practicing evacuation and rescue procedures. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Spreading knowledge about fire risks and prevention. |
The resilience displayed by these communities is a powerful reminder that, while the challenges posed by climate change are formidable, local populations are not powerless. Thay are harnessing their collective strength, ingenuity, and knowledge to build a future that not only survives but thrives in the face of adversity. This local action is vital in providing a template for other regions facing similar environmental challenges.
Innovative Solutions for Preventing Future wildfires
In the wake of escalating wildfires that ravage the landscapes of South America, innovative solutions are vital in mitigating these environmental disasters. It is indeed essential to adopt a multi-faceted approach that combines technology, community engagement, and sustainable practices to prevent future occurrences.
One promising strategy lies in the integration of advanced monitoring systems. Utilizing satellite imagery and drones, authorities can gain real-time insights into fire-prone areas, allowing for quicker response and targeted prevention strategies. These technologies contribute to:
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms can analyze climate patterns and past fire data to assess potential fire risks.
- Early Detection: Drones equipped with thermal sensors can spot hotspots before they escalate into large fires.
- Resource Allocation: Data-driven insights enable efficient deployment of firefighting resources where they are needed most.
Additionally, fostering community involvement is crucial. Grassroots campaigns that educate and empower local populations to engage in fire prevention methods can have a lasting impact. This includes:
- Firebreak Creation: Communities can participate in building firebreaks—cleared areas that stop the progression of wildfires.
- Tree Planting Initiatives: Reforestation efforts not only restore ecosystems but also serve as a barrier against the wind-driven spread of fires.
- Awareness Programs: Workshops that teach sustainable land management practices to local farmers can reduce the incidence of accidental fires.
Combining technology with community-driven efforts presents a robust framework to combat the growing threat of wildfires. As South America continues to grapple with the crisis, these innovative measures will be essential in restoring balance to the environment and ensuring the safety of its inhabitants.
Global Responsibility: The Role of International Cooperation in environmental Protection
The recent environmental crises in South America, characterized by rampant wildfires and worsening air quality, underscore the urgent need for international cooperation in addressing environmental challenges. Countries cannot combat these pressing issues in isolation; rather,a concerted global effort is essential. Multilateral agreements,such as the Paris Agreement,play a pivotal role in setting a framework for nations to collaborate,share resources,and implement joint strategies aimed at mitigating climate change and preserving biodiversity.
In this context, key components of successful international cooperation include:
- Shared Knowledge and Technology: Wealthier nations can aid developing regions by sharing sustainable agricultural practices and advanced firefighting technologies, which are crucial in combating wildfires.
- Financial Assistance: Providing funding to nations affected by environmental disasters can help restore ecosystems and rehabilitate communities affected by environmental degradation.
- Joint Research Initiatives: Collaborative scientific studies aimed at understanding the impacts of climate change can yield better strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
| Country | Recent Initiatives | Future Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Increased fire monitoring and enforcement of deforestation laws | Achieve zero deforestation by 2030 |
| Argentina | Investment in sustainable agriculture practices | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2025 |
| colombia | strengthening protected areas and reforestation projects | Restore 1 million hectares of forests |
Collaborative efforts extend beyond mere agreements; they involve genuine partnerships between nations, NGOs, and local communities. By fostering transparency and accountability, participating countries can not only mobilize resources more effectively but also ensure that commitments translate into meaningful action on the ground. The devastating impact of environmental neglect is evident, as seen in the skies over South America; thus, it is imperative that all stakeholders join hands in this global endeavor to safeguard our planet.
In Conclusion
As South America grapples with unprecedented wildfires that ravage its landscapes and communities, the consequences of environmental neglect and climate change become increasingly stark. The smoke that now blankets vast regions serves as a haunting reminder of the urgent need for action and awareness. These devastating fires not only threaten the rich biodiversity of the Amazon and the livelihoods of countless individuals, but they also underline a global crisis that transcends borders.
As we reflect on the environmental plight of South America,it is clear that the actions taken today will determine the trajectory of our planet’s health for generations to come. Policy changes, conservation efforts, and international cooperation are imperative to combat this escalating emergency. The Earth calls out for help, and it is incumbent upon us to listen and respond with not just sympathy, but with decisive action that addresses the root causes of these catastrophic events. The time for change is now—our planet’s future depends on it.
