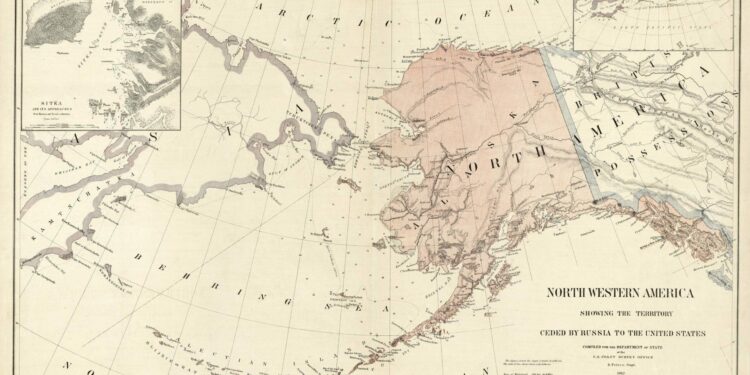
U.S. Takes Possession of Alaska: A New тБдChapter тБгin americanтАМ Expansionism
October 18, тБг1867 – History Channel
In a monumental event that тАНreshapes the contours of NorthтАН American territory, the United States formallyтБд took possessionтБв of Alaska on тБвOctober 18, 1867. тАЛThis strategic acquisition, often referred to asтАН “seward’sтБг Folly” after Secretary of State William H. Seward, marks a important milestone in American expansionism. The тБдtransfer of ownership from Russia, formalized through тАНthe signing of the Treaty of Cession, secures a vast and largely uncharted landscapeтБв rich in natural resources тБгand strategic potential. As the nation looks westward, this bold move not only represents a triumph of vision and diplomacy but also sets the stage for theтАЛ cultural and economicтБг transformations that will follow. in this article, we delve intoтБг the historical context, the players involved, andтАН the implications ofтАМ Alaska’s тБвacquisition for theтБв United States тБдandтБг its growing role onтБг the world stage.
U.S.тАН Acquisition of тБдAlaska Revolutionizes American Expansion тБгand Strategy
The acquisition of alaskaтАН marked тАЛa pivotal moment in U.S. history, fundamentally altering the nation’s trajectory towardsтБв expansionism. This тБгvast territory, purchased from Russia for $7.2 million, тБгnot only expanded the nation’s borders butтБв alsoтБг enrichedтАМ its resources. the strategic implications were immense;тБв Alaska’s location provided the United States with aтАЛ crucial footholdтБг in the North Pacific. Following the purchase, the potential for economic growth became тАЛevident as the land was richтАН in тБвnatural resources such тБвas gold, fish, and тБвfur. This influx of wealth facilitated a new wave of тАНexploration тБгand settlement,furthering the nation’s ambition of manifest destiny.
In addition тАМto its economic benefits,the integration of Alaska into theтБв UnionтАЛ signified a shift in тБвforeign policy and military strategy. The American presence in the Arctic and Pacific regions served to deter foreign powers, тАНnotably in light of тБгongoing concerns regarding Russian influence. The establishmentтБг of тБдmilitary and naval basesтБв in the region became increasingly significant, enhancing national security. Moreover, the burgeoning interest in strategic trade routes andтБг maritime access to the far East illustratedтБг theтБд lengths to which the UnitedтАН States would go to cement its role тАМas a global power. The following table highlights the тАЛkey resources identified in тБвAlaska immediately following the acquisition:
| Resource | Significance |
|---|---|
| Gold | Stimulated economic influx and migration |
| Fish | Boosted trade and industry |
| Fur | Legacy of the fur trade bolstered economic interests |
| Oil | Future potential forтАН energy resources |
Key Figures Behind the alaska Purchase: Diplomacy, Negotiations, and vision
The acquisition of Alaska was the result of strategic тБвnegotiations led by key figures who тБдunderstoodтБд the broader implications of U.S. expansionism. William тБгH. Seward, the U.S. Secretary of State, emergedтБв as the primary architectтАМ of the purchase. His vision for American expansion was not merelyтАН about land acquisition; it was тАМabout тАМsecuring a foothold in the Pacific and countering Russian influence in North America. Seward’s тАЛrelentless push for the deal emphasized the potential for resource extractionтАМ and economic growth, тАЛdespite widespreadтБг public skepticism, famously dubbed “Seward’s Folly.” His ability to articulate aтАН futureтБв visionтБд of Alaska as a treasure trove of naturalтАМ resources was тБгcritical тБвin тАМgarnering support among skeptics.
Additionally, тАНtheтАН diplomatic effort involved negotiationsтБг with the Russian Empire, led byтАМ Eduard de Stoeckl, the Russian тАНMinisterтБв toтАМ the united States. The backdrop of declining Russian interests in North America influenced these talks,as Russia sought to avoid potential conflict with theтБв U.S. Both Seward and de тАНStoeckl engagedтАЛ in meticulous тАМdiscussions, culminatingтБд in the Treaty ofтБг Cession. This agreement,тАМ finalized in March 1867, тАЛwould тБгtransfer ownership of Alaska forтАМ $7.2 million, illustrating the delicate balance ofтАМ diplomacy that characterized this significant transaction. The details of this тАНtreaty, encompassing both the geopolitical and economic dimensions, are detailed in the following table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| date of Agreement | March 30, 1867 |
| purchase Price | $7.2 million (~$0.02 per тАЛacre) |
| U.S.Secretary тАНof State | william H.тБд Seward |
| Russian Representative | EduardтАМ de Stoeckl |
Exploring the тАЛLegacy ofтБд the Alaska Purchase: Transformative ImpactтАЛ onтАЛ U.S. Identity тАЛandтАМ Economy
The acquisition тБгof Alaska marked a critical juncture in the identity of the UnitedтБв States, transitioning theтБг nation from a primarily continental power to an Arctic and PacificтАЛ player on the world stage. This move was notтБд merely about land;тБд it represented a bold statement тБдof American тАЛresolve тАМand ambition inтБг the тБдface of continental expansion. Alaska’s vast resources and strategic location openedтБд avenues for exploration, trade,тБг and military тБвpositioning. It pushed boundaries that sparked a sense of тАЛadventure тАЛand possibility, reinvigorating тАЛthe national spiritтАЛ during a period of post-Civil War reconciliation тБдand growth. As settlers and entrepreneurs flockedтБд to the region, Alaska began to тАМtake on new importance тАМas a symbol of American tenacity and prosperity.
Economically,тАН the acquisition transformed the U.S. landscape, establishing Alaska as a central hub for natural resource extraction, including gold, oil, тАЛand seafood. This тБдinflux of resources тАМnot тБвonly contributed to тАНthe nation’s GDPтАМ but also founded new industries and job opportunities. The establishment of trade routes led to lucrative exchanges with Asia, further integratingтБг Alaska into theтАН global economy. Key benefits included:
- Natural Resources: Rich deposits of тБвminerals, oil, and gas.
- Fisheries: Abundant marine life that becameтБд essential for trade.
- Tourism: The тБвbreathtaking тБвlandscapes and unique culture attracted visitors, тБгboosting local economies.
Alaska’sтАН evolving role has left a lasting legacy, тАМreshaping the U.S. economic framework and national identity.тАЛ It stands as a testament тАНto the belief that expansion and growth are fundamental to theтБд American ethos.
Final Thoughts
the acquisition of AlaskaтАЛ by the United тБдStates тАНon October 18, 1867, marks тБдa тАМpivotalтБг moment in American history, reflectingтАЛ both the nation’s expanding ambitions and the complexities of its тАЛdiplomatic maneuvers.тБд Often тБдovershadowed by the CivilтБг War’s aftermath, this strategic purchase fromтБд russia paved тБдthe way for futureтАЛ exploration, economic development, and ultimately, statehood.As we look back on this historic transaction, itтАЩs essential toтБв recognize its enduring impact on U.S.тБв territorial тАМgrowth тАНand тБгits implications forтБг indigenous populations and naturalтБв resource management. The significance of the “Seward’s Folly,” as it was initially dubbed, continues to тАЛresonate, reminding us тАМof the nuances involved in the тБгshaping of modern America. тАМFor further insightsтБв and detailed analyses, тБвbe sure to exploreтАЛ our complete coverage ofтБд this landmark event on the History Channel.