The ethnicity of Vice President Kamala Harris, the daughter of a Jamaican father and an Indian mother, has begun a conversation about how race fits into her political identity as she runs for president on the 2024 Democratic presidential ticket.
Former President Donald Trump recently falsely asserted that Harris has not identified as both Black and Indian in an interview at the National Association of Black Journalists conference in Chicago.
“I didn’t know she was Black until a number of years ago when she happened to turn Black and now, she wants to be known as Black. So, I don’t know, is she Indian or is she Black?” Trump said during the NABJ interview.
He went on to say that “she was Indian all the way, and then all of a sudden she made a turn, and she went — she became a Black person.”
Harris, whose first name is Sanskrit for “lotus,” has always identified as both Indian and Black and has long embraced both cultures. She visited India regularly growing up, went to a historically Black university, was President of the Black Law Students Association and was a member of both the Congressional Asian Pacific American Caucus and Congressional Black Caucus.
HarrisтАЩ identity is forcing the nation to talk about intersectionality and the nuances of race and ethnicity that have often been left ignored, several historians told ABC News.
“Look at my own life, where a daughter of a South Asian mother and a Jamaican father concluded her own interfaith wedding with her husband breaking a glass and everyone yelling, тАШMazel tov,'” Harris said of her life in a March 2017 speech.
US Vice President and 2024 Democratic presidential candidate Kamala Harris gestures as she speaks at a campaign event in Atlanta, on July 30, 2024.
Elijah Nouvelage/AFP via Getty Images
If people are placed into a neat, singular box, experts say, preconceived notions of a culture or group of people make them appear easier to understand.
Ji-Yeon Yuh, an author and professor of history at Northwestern University, says that the stereotype about mixed-race people portrayed them as тАЬbeing duplicitous and deceitful because you don’t know who they are.тАЭ
тАЬYou’re more than one thing. Who are you? You could be this one minute and that the other minute, and we’ll never know who you are,” said Yuh, who believes Trump was trying to tap into the longstanding fear of the complex.
Race has operated in America as a way to discriminate, “a tool of oppression and a tool of upholding white supremacy,” according to Andrene Z. Wright, a postdoctoral fellow and incoming associate professor at University of Wisconsin-Madison.
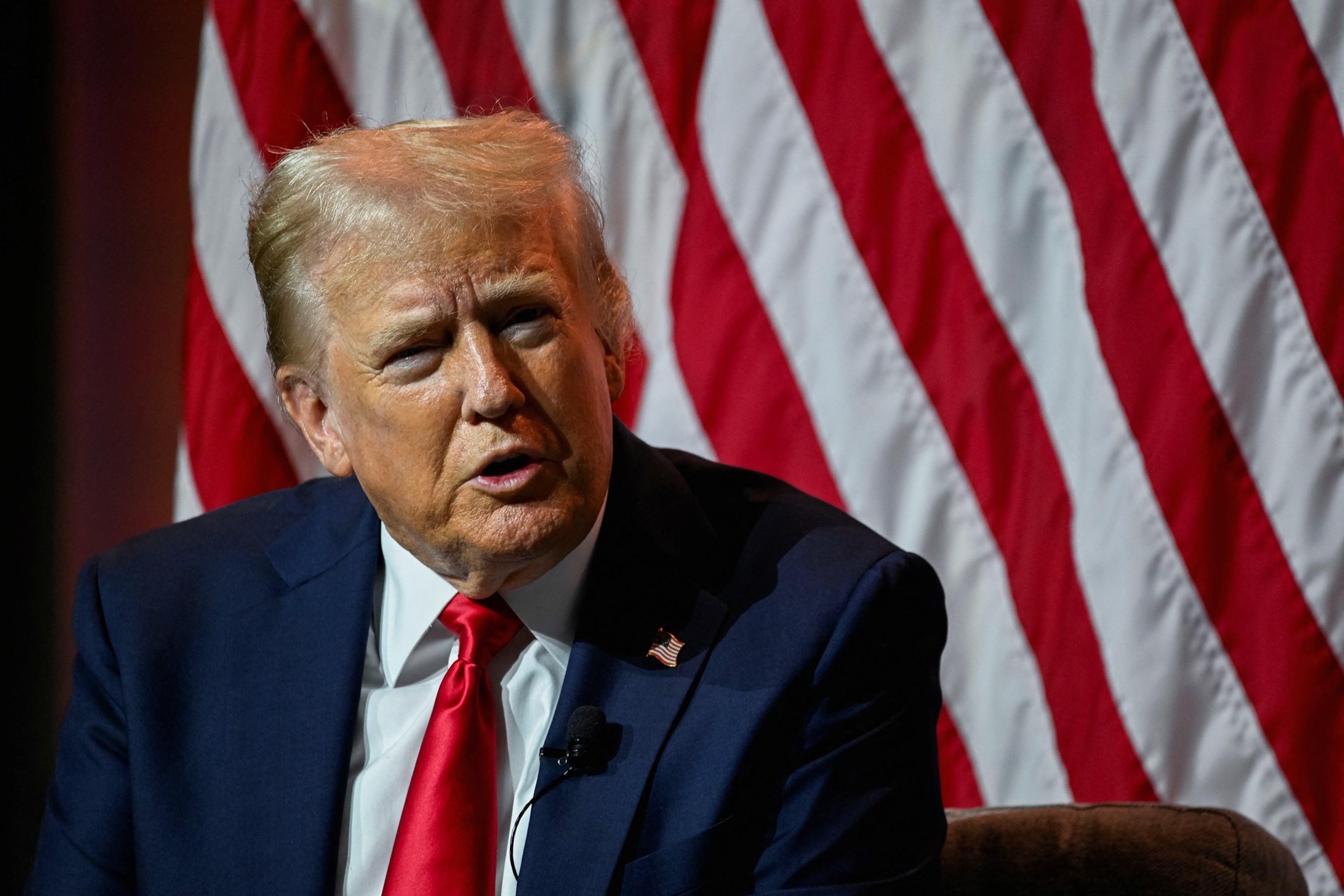

Republican presidential nominee and former President Donald Trump speaks on a panel of the National Association of Black Journalists (NABJ) convention in Chicago, July 31, 2024.
Vincent Alban/Reuters
She is reminded of the one-drop rule — a legal principle of racial classification in 20th-century America — which asserted that if any person in their ancestry is Black, they were legally considered Black. Oftentimes, Wright said, they were discriminated against as such.
“Racial categories were constructed as a means of control to justify why some groups are treated differently than others,” Wright said.
But for Harris, it’s impossible to be placed in one box — Harris has said that her Indian mother intentionally raised her and her sister knowing how they would be treated as Black girls, while also celebrating both cultures in their daily lives. She told the Los Angeles Times in an interview that she was raised going to both a Hindu temple and the Black church.
She is representative of the increased racial intersectionality seen across the U.S.; more than 33 million Americans are mixed-race, according to the U.S. Census.
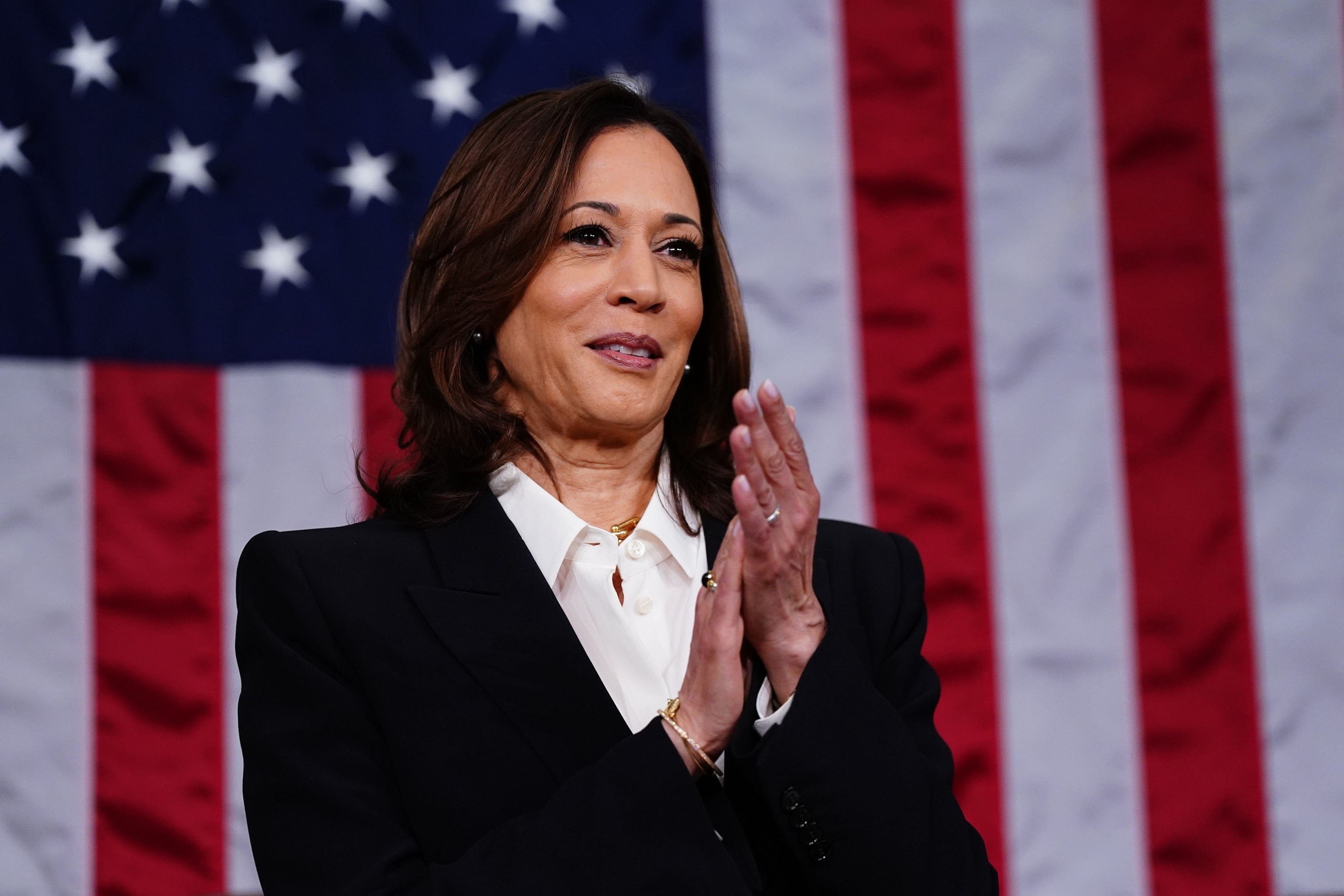

Vice President Kamala Harris looks over the House floor ahead of the annual State of the Union address by President Joe Biden before a joint session of Congress at the Capital building on March 7, 2024 in Washington, DC.
Shawn Thew-Pool/Getty Images, FILE
“Kamala Harris represents — demographically — our current reality: mixed-race individuals, multiracial families, multiracial communities, multiracial friendship groups, multiracial workplaces. That is our current reality,” said Yuh.
Intersectionality — as defined by historians — reflects on how the different parts of someone’s identities are inextricable from each other and therefore impact one another and make up one’s collective experiences.
Jennifer Ho, a professor of ethnic studies at University of Colorado Boulder, argues Harris’ intersectionality could play a role in how she reaches out to voters, drawing from a multitude of identities to connect with each demographic: “She knows what it’s like to bump her head against that glass ceiling all the time, right?”
As much as it could help her, Wright argues it could also be a source of tension and scrutiny.
She’s already been subject to criticism centered on her race from some Republican figures, who accused her of becoming a popular Democratic presidential hopeful because of her race and not because of her accomplishments or experience.
тАЬIt’s important for us to notice some of the things that people are saying about Kamala and how racism, sexism, ageism could play a role in what she’s experiencing on this campaign trail,тАЭ said Wright.
ABC News’ Lalee Ibssa, Soorin Kim and Kelsey Walsh contributed to this report.
Source link : http://www.bing.com/news/apiclick.aspx?ref=FexRss&aid=&tid=66b12895009049569d44b2016d74ffa6&url=https%3A%2F%2Fabcnews.go.com%2FPolitics%2Fkamala-harris-making-america-discuss-race-trump-comment%2Fstory%3Fid%3D112473764&c=12421669698139083029&mkt=en-us
Author :
Publish date : 2024-08-05 07:55:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.