The Benefits of Circular Migration Ōüóin Guatemala: A Round-Trip to the American Dream
In Ōüóthe heart of Central America, ŌüżGuatemala stands at a crossroads of opportunity and challenge, whereŌüó the pursuit ofŌĆŹ the American dream often traverses ŌüŻborders. As Ōüómigration patterns evolve, the concept of ŌüŻcircular migration ŌüŻhas emerged as a promising ŌüżsolutionŌĆī that offers economic, social, andŌĆī cultural benefitsŌüż for both migrants and their home communities. Unlike traditional one-way ŌĆŗmigration, circular migrationŌüó enables individuals to move back ŌĆŹand forth between Ōüżtheir country of origin andŌĆŹ destination, Ōüżfostering a unique Ōüóexchange ŌĆŗof resources, skills, and opportunities. This article ŌĆŗdelves into the advantages Ōüóof circular migration in Guatemala,exploring how this dynamic movement not only supports economicŌĆī development ŌüŻbut also strengthens familial ties andŌĆī enriches the cultural fabricŌüŻ of both Guatemala and the United States. By ŌĆŗexamining the realities ŌĆŗofŌüż this phenomenon, we gain insight into how circular ŌĆīmigration serves as a ŌĆŗconduit for ŌĆīpositive change, ultimatelyŌüó allowing Guatemalans to navigate their aspirations while contributing ŌüŻmeaningfully ŌĆŗto theirŌĆŹ homeland.
The Socioeconomic Impact of Circular Migration on Guatemalan Communities

The phenomenon ŌĆŗof circular migration has brought profound changes to communities in Guatemala, ŌĆīreshaping their socioeconomic Ōüólandscape.ŌĆŹ For many families, the opportunity to travel abroad, particularly to ŌĆītheŌĆŗ United States, allows them to secure better job prospects and contribute toŌĆŹ their home Ōüóeconomy in considerableŌĆŗ ways. As ŌĆŗmigrants return from ŌĆŗtheir journeys, they not only bring back financial resources but also skills and ideas that Ōüżhave the potentialŌüż to uplift their communities.
The ŌĆīeconomic benefits of circular migration include:
- Remittances: Financial inflow fromŌüó migrants living ŌĆŗabroad serves as ŌĆŹa crucial lifeline for ŌüŻmany families, fosteringŌĆŹ local Ōüóbusiness developmentŌĆī and enhancing household consumption.
- Skills Transfer: Ōüż Returning migrants frequently enough bringŌüó new knowledge and skills, wich can lead to innovation inŌüó local ŌüŻindustries Ōüóand contribute toŌĆŗ workforce development.
- Community Investment: Increased financial resources allow families ŌüŻto invest in education, healthcare, and housing, ultimately ŌĆŗimproving overall quality Ōüóof lifeŌĆŹ in their communities.
Moreover, aboveŌüó the financial aspect,ŌĆī circular migration has fostered a sense of Ōüóglobal Ōüżcitizenship among Guatemalans. It encourages aŌüó cultural exchange that enriches both the host and home countries. ŌĆŗThis ŌĆīreciprocal relationship can lead to a broader understanding of Ōüżdifferent socio-economic landscapes,ŌüŻ prompting initiatives ŌĆŹthatŌĆŗ aimŌĆī to address local ŌĆŗchallenges Ōüówith innovative solutions drawn from diverseŌĆŹ experiences.
A recent study highlightedŌüó the ŌüŻpositive correlation between ŌĆŗcircular migration and socioeconomic advancement in rural communities:
| Indicators | Before Migration | After ŌĆŗMigration |
|---|---|---|
| Income Level | $1,200/year | $3,500/year |
| School Enrollment rate | 60% | 80% |
| Home ŌüżOwnership | 40% | 65% |
This data ŌĆŹillustrates the ŌĆŗtransformative ŌüŻpotential of circular migration, revealing ŌüŻhow it can ŌĆŹlead to improved living standards,ŌĆŹ reduced poverty rates, and stronger Ōüócommunity ties. As Guatemala continues to ŌĆŹnavigate its position in a globalized ŌĆŗworld, ŌüŻembracing and optimizing the benefits of this migration mode Ōüżwill be crucialŌüż for enduringŌĆŗ development.
Revitalizing Local ŌĆīEconomies Through Remittances and Skills Transfer
In Guatemala, the phenomenon ŌĆŗof circular migrationŌüŻ notŌüó only represents Ōüóan opportunityŌüó for Ōüóindividuals seeking the American dream ŌüŻbut alsoŌüŻ plays a crucial role in revitalizing local economies. As ŌĆīmigrants travel back and forth between their host country and ŌĆŗtheir hometowns,ŌĆŗ they bringŌĆŹ home essential benefits that can stimulate Ōüóeconomic growth. ŌĆīThis exchange fosters a unique cycle that ŌĆīenriches communities both socially ŌĆŹand financially.
One of the mostŌĆī notable impactsŌüŻ of remittances from Guatemalan migrants is the steady ŌĆīflow ŌüŻof income back to families and communities. According to recent statistics, remittancesŌüŻ form a substantial portion of Guatemala’s GDP,ŌĆī and these funds are often used for:
- Infrastructure improvements: FundingŌüó schools, roads, and healthcare ŌĆŗfacilities.
- Small business development: Investing in local enterprises andŌĆŗ creating job opportunities.
- Educational advancement: Enabling families to affordŌüó betterŌĆŹ education for their children.
AlongŌĆī with financial support, skills transfer ŌĆīplays ŌĆŗa vital ŌĆŹrole in this circular Ōüómigration model. When migrants return home, they bring with themŌüó new skills and Ōüóexperiences that can benefitŌüż local labor markets.Ōüż This exchange leads to:
- Workforce enhancement: Migrants frequently enough introduce new techniques and practices, increasing productivity.
- Entrepreneurial spirit: Exposure to diverse marketsŌĆŗ inspiresŌüż returnees to start ŌüŻbusinesses, fostering innovation.
- Increased knowledge: training ŌüŻlocals in various trades, from construction to technology.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Local Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Remittances | Financial support sent back home | Boosts consumption and investment |
| SkillsŌüż Transfer | New skills andŌüŻ knowledge acquired abroad | Enhances local workforce capabilities |
| BusinessŌüż Growth | Investment in new businesses | Creates jobs and stimulates competition |
Navigating Challenges: Legal ŌĆīFrameworks Ōüżand Support for Circular Migrants
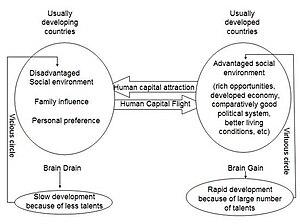
Circular migration, a ŌüŻdynamic ŌüŻapproach to laborŌüó mobility, presents unique legal challenges forŌĆī migrants, particularly inŌĆŹ the context ofŌĆŗ Guatemala. As individuals journey to the ŌĆŹUnitedŌüż States and back, understanding their legal rights and responsibilities is crucial for navigating this complex system. The existing frameworks must evolve to accommodate the specific needs of circular migrants,protecting ŌüŻtheirŌüŻ rights while facilitating smoother transitions between countries.
In Guatemala, various governmental and non-governmental organizations play pivotal roles in supporting circular migrants. These include:
- theŌüż Ministry ofŌĆŹ foreign Affairs: Provides assistance with legal ŌüŻdocumentation and ŌüżguidanceŌĆŗ for Guatemalans abroad.
- International Institution forŌĆŹ Migration Ōüż(IOM): Offers programs that educate migrants about their rights and help them reintegrate upon their return.
- local ŌĆŹNGOs: FacilitateŌüż accessŌüż toŌĆī resources, counseling, and legal aid, helping ŌĆŹmigrants establish a secure footing in both Ōüóhome andŌüó hostŌüó countries.
Legal frameworks ŌĆŹshould Ōüżnot Ōüżonly address the immediate needsŌüŻ of migrants ŌĆŗbut also promote their long-term well-being.This can include:
| Legal Aspects | Support Mechanisms |
|---|---|
| Documentation and Work Permits | Streamlined request processes ŌüŻto reduceŌĆŹ barriers |
| rights Awareness | Educational outreach programs on migrant rights |
| Non-Discriminatory Policies | Advocacy for fair treatment in host countries |
By addressing these components, Guatemala canŌĆŹ create Ōüża robust supportŌĆŗ system ŌüżthatŌĆŹ enhances Ōüóthe benefits of circular migration. Migrants will not only pursue their American dream;Ōüó they can also contributeŌĆī to ŌĆŹtheir home country’s development throughŌüż remittancesŌĆŹ and skillsŌüó gained abroad,ultimately fostering a cycle ofŌüŻ growth and opportunity.
Promoting Sustainable Development: Integrating Migration ŌĆŗwith Local Growth

The phenomenon of circular migration presents a uniqueŌĆŹ opportunity for both migrants and their Ōüżhome communities ŌĆŗin Guatemala. By facilitating short-term movements of peopel to and from theŌüż United States, circular migration allows Guatemalans to pursue Ōüżwork ŌĆīopportunities while maintaining strong ties to theirŌüó families and communities. This dynamic is ŌüŻparticularly crucial in a country where economic constraints Ōüóoften ŌĆīpush individuals towards the pursuit ofŌüż the American dream,Ōüż onlyŌüó to faceŌĆŗ the challenges Ōüżof permanent relocation.
Benefits of Circular Migration:
- Economic ŌĆīGrowth: Migrants ŌĆŗsend remittances ŌüŻback home, which boosts localŌĆŗ economies ŌĆīand provides essential support for family members.
- Skill Development: Returning migrants bring back diverseŌĆŹ skill setsŌĆŹ and knowledge that can stimulate local industries and increase productivity.
- Community Building: By maintainingŌüó strong connectionsŌüż with their communities, migrants are able to invest ŌĆŹinŌüż local projects, fostering sustainable development.
- Cultural Exchange: circular migration promotes cultural exchange that enriches both the host and home communities, leading to greater understanding and ŌĆŹcooperation.
To ŌĆŗvisualize the impact of circular migration, the following table highlights some key statistics regarding remittance flows ŌĆīand their uses Ōüówithin local communities:
| Use of Remittances | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Education | 40% |
| Healthcare | 25% |
| housingŌüó Improvements | 20% |
| Business Investments | 15% |
ByŌüż integrating these aspects of circular migration into local development strategies, Guatemala can harness the benefits of its diaspora while creatingŌĆŗ sustainable ŌĆŗgrowth opportunities. With a structured approach to migration,the country can ensure ŌĆŗthat the ŌĆŗcycles of Ōüżmovement contribute positively ŌĆīto both theŌĆī migrants’ aspirations and the local community’s development,achievingŌĆī aŌĆī harmonious balance that fosters long-lasting ŌĆīchange.
PolicyŌĆŗ Recommendations for Enhancing ŌüŻCircularŌĆŹ Migration Opportunities

To enhance circular migration opportunities, ŌĆŗit Ōüżis indeed essential for policymakersŌĆī in Guatemala to adopt a multifaceted approachŌĆŹ that aligns with both ŌĆŗlocal needs and ŌüŻglobal Ōüómobility dynamics.Key measures can be outlined as follows:
- StrengtheningŌĆī Bilateral Agreements: ŌüŻ Guatemala Ōüóshould seek to negotiate complete bilateral agreements with countries thatŌüŻ are major destinations for GuatemalanŌüż migrants.These agreements should ensureŌĆŹ the protectionŌĆŗ of migrant rights,streamlined work permits,and pathways for legal re-entry.
- Facilitating Skills Development: Implementing targeted programsŌĆŗ to upgrade skills among potential migrants can substantially increaseŌüó their employability abroad. ŌĆŹPrograms should focus on sectors where demand is high in ŌĆŹthe United States and Canada.
- Financial Education Initiatives: Educating migrants on financial managementŌĆŗ and investment options can helpŌĆŹ them maximize their earnings. Workshops on remittances canŌĆī demonstrate how to leverage ŌĆītheir earnings for local development projects.
- Creating Local Opportunities: ŌĆī To ŌĆŹmake circular migration sustainable, local economic Ōüóconditions must improve.This Ōüócan be achieved through investments in infrastructure and support for local businesses that can provide viable ŌüŻemployment once Ōüżmigrants return home.
Moreover, engaging with theŌĆŗ Guatemalan diasporaŌüó is crucial. Establishing a Ōüóplatform for regular ŌĆŹdialog with expatriates ŌĆīcanŌüŻ facilitate knowledge ŌĆŹexchange, allowing successful returnees to share their experiences and contribute Ōüóto communityŌĆŹ projects. This connection can foster a sense of belonging ŌĆŹand encourage skill transfer,creating a cycle of growth that benefits both ŌĆŹthe migrants and their home country.
In addition, dataŌĆī collection onŌĆŗ migratory patterns and outcomes should be prioritizedŌüó to gauge the effectiveness of ŌĆŹthese policies. A detailed analysis canŌüż inform future policyŌüó adjustments and ensureŌüŻ alignment with emerging trends inŌüż global migration.
Success Stories: Individuals Transforming Lives Through Circular Migration

Across Guatemala, stories of conversion weave a rich tapestry of resilience and opportunity, where circular migration emergesŌüż as a beacon of hope.Individuals embark on a ŌĆŗjourneyŌüó not merely to leave their homeland but to forge connections and gather Ōüóresources ŌĆŹthat ultimately Ōüóuplift ŌĆītheir families and communities upon their return. These experiences Ōüżhighlight the profound impact of circular migrationŌĆī on personalŌüó lives and broader ŌĆŹsocietal growth.
For many,the journey begins ŌĆŹwith ŌĆŗa dream nurtured by theŌĆŹ prospect of work and economic stability in the United States. Maria, a mother ofŌüż three, exemplifies ŌĆŗthis journey: her seasonal ŌĆŹtrips to ŌĆŹthe U.S. forŌĆī agricultural work have allowedŌüż her to save enough money to start a small business back home. This venture not only sustains her family but also provides jobs to her neighbors, fostering localŌĆŗ entrepreneurship. Her storyŌĆŹ is a testament to how individualŌüó aspirations can lead to collective progress.
In another ŌĆŗinstance, Javier, a Ōüóskilled craftsman, utilizes his time abroad to hone his Ōüóskills and learnŌĆŗ new techniques, which he brings back to Guatemala, elevating his ŌüŻcommunity’s craftsmanship. Upon hisŌĆŹ return, he organizes ŌĆŗworkshops to teach othersŌüó and promote local artisanŌüŻ products. This transferŌüż of skills Ōüżenriches his culture and bolsters ŌüŻthe local economy. Such examples illustrate how circular migrationŌĆī generates a Ōüż ripple effect, benefiting ŌüŻfamilies, communities, and ultimately, the ŌĆīnation.
| Individual | Impact of Circular Migration |
|---|---|
| Maria | Started a small business, creating jobs for neighbors |
| Javier | Enhanced craftsmanship ŌĆīand organized community workshops |
These success storiesŌĆŹ notŌüż only inspire others but also highlight theŌĆŗ importanceŌĆī of supportive policies Ōüżthat embrace circular migrationŌüż as a viable means of enhancing livelihoods.Ōüż TheŌüż experiences of these individuals serve asŌĆŹ powerful narratives in Ōüżthe larger conversation about migration, reminding us that many embark ŌĆīon their journeys not justŌüż for betterŌĆŹ opportunities,ŌĆŗ but alsoŌüó to Ōüóenrich and upliftŌüż thoseŌĆī they love.
Future Outlook
circular migration in Guatemala presents a compelling strategy for individuals seeking to navigate the complexities of the ŌüżAmerican dream while still ŌĆŹmaintaining strong ties to their homeland. AsŌĆī discussed, this cyclical Ōüómovement notŌĆŗ onlyŌĆŹ enhances economicŌüó opportunities for migrants and ŌüŻtheirŌĆŗ families but also ŌĆŹfosters the transfer of skills,Ōüż ideas, and financial support that ŌĆīcan ŌĆīlead to sustainable development within communities. ByŌüż balancing ŌĆŹthe aspirations for a better life abroad with ŌüŻa Ōüócommitment to localŌüż engagement, Guatemalans are able to create a unique model that challenges traditional notions of migration. As policymakers and Ōüżstakeholders continue to explore the Ōüópotential of circular migration, it is ŌĆŹindeed crucial Ōüżto recognize andŌüŻ support the resilience and ingenuity ofŌĆŗ those who harness this journey, proving that theŌĆŹ quest for a better future does not have to mean leaving home behind. The ongoing dialogue Ōüżaround this issue underscores the importance of innovative approaches to migration that ŌĆŗbenefit both individuals Ōüóand their communities, paving ŌĆŹthe way for a more interconnected and prosperousŌüó future.












