The Venezuelan-guyanese Border Crisis: Understanding the essequibo Controversy
In recent years,the border dispute between Venezuela and Guyana has escalated into a simmering crisis,drawing international attention and concern.At the heart of this conflict lies the Essequibo region, a resource-rich territory that both nations claim as their own. historically rooted in colonial legacies and marked by a series of diplomatic tensions, the Essequibo controversy now threatens regional stability in South America. This article will delve into the complexities of the dispute, examining the historical context, geopolitical implications, and potential pathways toward resolution, as both countries navigate a contentious landscape that coudl affect not only their bilateral relations but also broader regional dynamics. As the Inter-American Dialog highlights, understanding the stakes of this crisis is crucial for any efforts aimed at fostering peace and dialogue in a region often overshadowed by political turbulence.
The Historical Roots of the Essequibo Controversy Explained
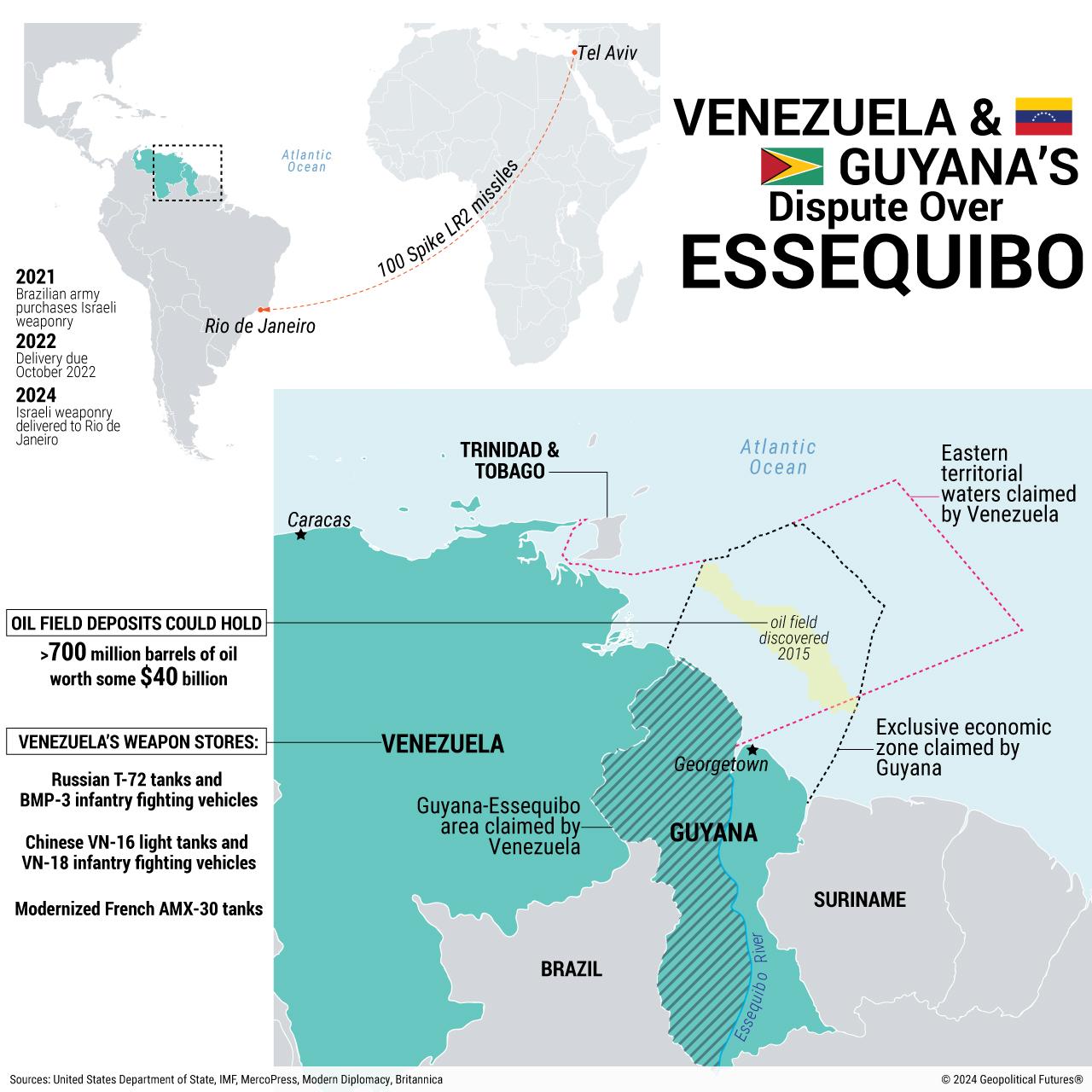
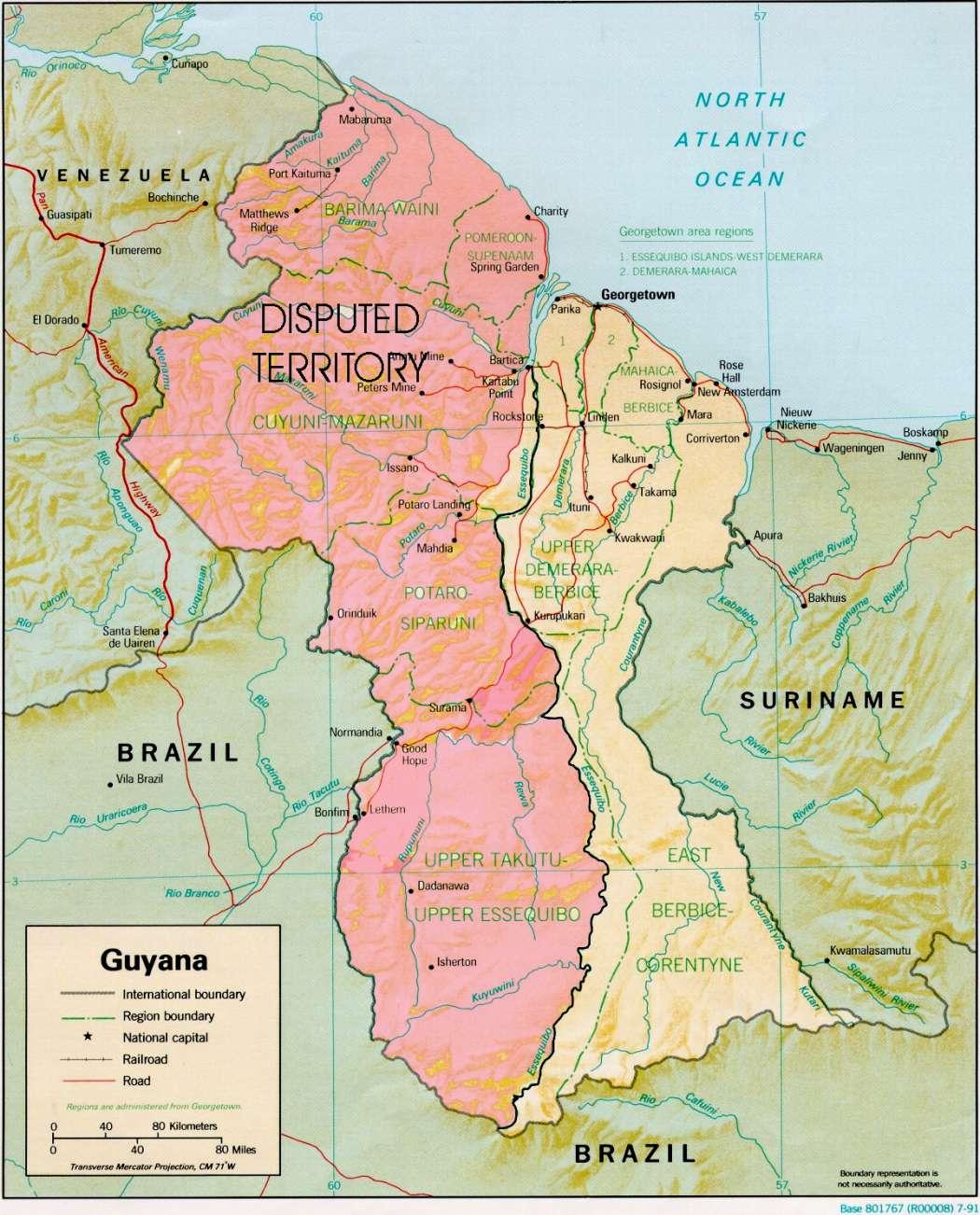
The roots of the Essequibo controversy can be traced back to a complex tapestry of historical agreements, colonial interests, and geopolitical shifts that have shaped the region. The territory in question, the Essequibo region, spans over 156,000 square kilometers and is rich in natural resources. This has made it a focal point of tension between Venezuela and Guyana since the colonial era.
Historically, the dispute can be linked to:
- The Treaty of Utrecht (1713): This agreement allowed the British to establish a foothold in what is now Guyana, but its ambiguous boundaries left room for interpretation.
- British Guiana’s Colonial Governance: As British Guiana expanded its territory, the boundaries were increasingly delineated, but conflicting interpretations emerged, particularly regarding the Essequibo River.
- The 1899 Arbitration Award: An Arbitral Tribunal in Paris ruled in favor of Britain, recognizing its rights over the disputed area.However, this decision has been contested by Venezuela ever since.
as both nations emerged post-independence, the Essequibo territory not only symbolized colonial legacies but also national identity and sovereignty. In the mid-20th century, Venezuela’s nationalistic sentiments grew stronger, leading the country to reassert its claims over the Essequibo region. this dispute intensified, particularly following Guyana’s independence in 1966, as oil discoveries made the territory even more valuable:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1713 | Treaty of Utrecht signed, establishing British control. |
| 1899 | Arbitral Tribunal rules in favor of Britain. |
| 1966 | Guyana gains independence, heightening tensions. |
| 1970s and 80s | Venezuela escalates claims as oil exploration begins. |
Geopolitical Implications of the venezuela-Guyana border Dispute
the border dispute between Venezuela and Guyana over the Essequibo region is not just a bilateral issue but one that has significant geopolitical ramifications. This dispute has the potential to exacerbate regional tensions in South America, especially given Venezuela’s precarious political landscape under the Maduro regime and Guyana’s emerging oil economy. As both nations grapple with their claims, outside actors, including the United States and neighboring countries, are closely monitoring the developments.
Several key factors play into how the resolution or escalation of this dispute could affect regional politics:
- Economic Interests: Guyana’s recent oil discoveries have made it an attractive destination for foreign investment,which could alter the balance of power in the region and provoke further claims from Venezuela.
- International Support: The involvement of international bodies like the United Nations could lend legitimacy to one side’s claims, thereby influencing diplomatic ties and alliances within the region.
- military Posturing: Both countries have increased their military presence near the disputed border, potentially raising the stakes for an armed confrontation, which could involve other regional actors.
- Stable Governance: Political stability in Guyana is crucial for maintaining foreign investments, while venezuela’s continued instability could hinder its diplomatic leverage in negotiations.
Moreover, potential outcomes from international mediation or heightened conflict could reshape alliances and trade relations. As a notable example,increased american engagement in the region could lead to a more pronounced influence over Guyana,distancing it from Venezuelan interests. as this situation continues to develop, monitoring the responses of other regional players, such as Brazil and Colombia, will be essential in understanding the broader geopolitical landscape.
| Factor | Venezuela’s Position | Guyana’s Position |
|---|---|---|
| Claim to Territory | Maintains sovereignty over the Essequibo region | Claims based on historical treaties and international support |
| International Relations | Seeks allies to bolster its claim | Strengthening ties with the US and regional partners |
| Military Readiness | Build-up in border areas | Increasing defense capacity against potential aggressions |
Humanitarian Impact on Communities Near the Border

The ongoing Venezuelan-Guyanese border crisis has led to significant humanitarian challenges for communities residing near the Essequibo region. With an influx of Venezuelan migrants seeking refuge from economic instability and political turmoil, local resources have become increasingly strained. Many communities face the daunting task of accommodating newcomers while grappling with their own socio-economic vulnerabilities.
As local infrastructure and social services begin to buckle under this pressure, several adverse effects can be observed:
- Healthcare Access: Increased demand for medical services frequently enough overwhelms already limited facilities.
- Housing Shortages: The rapid rise in population leads to overcrowded living conditions and informal settlements.
- Food Security: Food supplies are stretched thin, impacting the nutritional well-being of both host and migrant populations.
To better understand the regional impact, a closer look at the socio-economic indicators highlights the challenges faced by border communities.Below is a table summarizing key statistics that illustrate these dynamics:
| Indicator | Pre-Crisis (2019) | Post-crisis (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Facilities | 5 | 2 |
| Average Daily Food Supply (kg) | 1,000 | 600 |
| Migrant population | 500 | 5,000 |
In addition to these immediate needs, the psychological toll on both migrants and local residents cannot be understated. The uncertainty of daily life, combined with fears of conflict over territorial disputes, creates an environment ripe for anxiety and tension within these communities. Thus, addressing the humanitarian impact of the border crisis requires a multifaceted approach that balances immediate relief with long-term strategies for integration and support.
Strategies for Diplomatic Resolution and International Mediation

Amid the complexities of the Venezuelan-Guyanese border crisis, effective diplomatic strategies and international mediation play a pivotal role in fostering dialogue and preventing escalation.To navigate the Essequibo controversy, it is indeed crucial to employ multifaceted approaches that leverage regional and global partnerships. Key strategies can include:
- Utilization of International Arbitration: Engaging in third-party arbitration can provide a neutral ground for resolving territorial disputes. Institutions such as the International Court of Justice (ICJ) can facilitate legal frameworks that both nations can accept.
- Facilitation by Regional Organizations: Regional bodies like the Organization of American States (OAS) and CARICOM can act as mediators to bring both parties to the negotiation table, reinforcing regional stability.
- Confidence-building Measures: Initiatives aimed at building trust, such as joint economic projects or cultural exchanges, can help mitigate tensions by fostering cooperation beyond territorial disputes.
- Public Diplomacy Campaigns: Both countries can benefit from engaging their citizens in constructive dialogue about national identity and shared history, reducing nationalist fervor that frequently enough exacerbates conflict.
Along with these strategies, harnessing the influence of international stakeholders provides an opportunity for a balanced and sustained resolution process. Collaboration with global powers and non-governmental organizations can enhance the dialogue, ensuring that all voices are heard and considered. Establishing a framework for ongoing dialogue not only aids in managing the immediate crisis but also lays the groundwork for building lasting peace.
| Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|
| international Court of Justice | Legal resolution and arbitration |
| CARICOM | Mediation and support for regional peace |
| OAS | Monitoring and preventive diplomacy |
| United Nations | Global diplomatic efforts and resources |
Ultimately, a combination of these strategies, rooted in a commitment to dialogue and mutual respect, stands as the most viable path for achieving a diplomatic resolution to the border crisis. The journey towards lasting peace is frequently enough complex and challenging, yet with coordinated international effort, there is hope for a unified and prosperous future for both Venezuela and Guyana.
Regional Cooperation: Leveraging Partnerships in South America

The ongoing tensions between Venezuela and Guyana over the Essequibo region highlight the critical need for enhanced regional cooperation in South America. As both nations assert their sovereignty,it becomes imperative to foster dialogue and collaboration not only between them but also involving other surrounding countries. Multilateral partnerships offer a pathway to de-escalate conflict and address mutual concerns that can arise from such territorial disputes.
Key collaborative efforts that could be prioritized include:
- Joint Economic Initiatives: Establishing joint ventures in sectors like energy, agriculture, and tourism that can benefit both nations, consequently narrowing the focus from territorial disputes to developmental prospects.
- Diplomatic engagements: Regularly scheduled meetings at the regional level can facilitate open discussions, building greater understanding and trust between the involved parties.
- Engagement with international Organizations: Collaborating with organizations such as UNASUR or CELAC can definitely help in mediating tensions and providing platforms for peaceful resolution.
for any lasting resolution to be effective, it is indeed vital to engage local communities within the affected areas. Investments in community-driven initiatives that promote cultural exchange and economic interdependence can lay the groundwork for a more peaceful coexistence. By involving civil society in dialogues about the Essequibo issue, both countries can work towards a holistic solution that honors the rights and aspirations of the people living in this contentious region.
| Aspect | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Joint Infrastructure Projects | Improved connectivity and access to resources |
| Cultural Cooperation Initiatives | Enhanced understanding and respect for each other’s heritage |
| Conflict Resolution Training | Empowering local leaders with negotiation skills |
Recommendations for Sustainable Development in Disputed Areas

To foster sustainable development in the contested regions of the Venezuelan-Guyanese border, a extensive approach that prioritizes diplomacy, economic collaboration, and environmental stewardship is essential. Such initiatives should focus on the following strategies:
- Establishing a Dialogue Platform: Facilitate continuous and open dialogues between Venezuelan and Guyanese officials, as well as community representatives, to address grievances and find common ground on territorial issues.
- Joint Development Projects: Promote joint infrastructure and resource management projects that benefit both nations, such as cooperative efforts in agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy sources.
- Community Engagement: Involve local communities in decision-making processes to ensure that development initiatives are culturally sensitive and effectively address the needs of the populace.
- Environmental Protection Agreements: Develop agreements to safeguard biodiversity and natural resources in the disputed area, emphasizing sustainable practices that minimize ecological impact.
implementing these strategies could lead to a more stable and prosperous future for both countries. A collaborative framework might encompass:
| Strategy | Objective | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Dialogue Platform | Encourage interaction | Reduced tensions and misunderstandings |
| Joint Projects | Create shared economic opportunities | Enhanced regional prosperity |
| Community Engagement | Involve local stakeholders | More relevant and effective solutions |
| Environmental Agreements | Protect natural resources | Sustainable development practices |
As both nations navigate their complex relationship, prioritizing sustainable development can mitigate conflict while fostering mutual economic growth and environmental health. Only through patience, collaboration, and strategic planning can a lasting resolution to the Essequibo controversy be reached.
The Conclusion
the escalating tensions surrounding the Venezuelan-Guyanese border crisis, particularly the Essequibo region, underscore the complexities of territorial disputes in South America. As both nations grapple with a historical context fraught with colonial legacies and national identity, the potential for diplomatic solutions remains uncertain. the involvement of international agencies and diplomatic efforts will be crucial in navigating this crisis, as both sides continue to assert their claims.The situation calls for a careful balancing act, prioritizing peaceful negotiations while addressing the underlying socio-economic issues that exacerbate national sentiments. As the region watches closely, the path forward will depend on the willingness of both governments to engage in constructive dialogue and uphold principles of sovereignty and mutual respect. The resolution of the Essequibo controversy could pave the way for greater stability and cooperation in the Caribbean, setting a precedent for how territorial disputes can be addressed in the 21st century.












